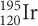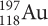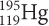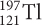LESSON 15: Nuclear Quest: Nuclear Reactions
THINK ABOUT IT
When the nucleus of an atom is changed in some way, a nuclear reaction is taking place. Nuclear reactions take place in the Sun and sometimes on Earth. Scientists can also make nuclear reactions happen in laboratories and in nuclear power plants.
What are nuclear reactions?
To answer this question, you will explore
Nuclear Changes
Radioactive Decay
Fission and Fusion
Nuclear Changes
EXPLORING THE TOPIC
Nuclear Changes

Changes in the nucleus are called nuclear reactions. Nuclear reactions differ greatly from chemical reactions. Nuclear reactions involve changes to the nucleus and can change one element into another element. The nucleus of an atom is not so easy to change.
Some nuclear reactions don’t require any help to get started. But changing the nucleus of an atom on purpose can require massive amounts of energy, so you would not be able to do this in your chemistry lab. There are several ways the nucleus of an atom can change. The nucleus can lose particles, it can be split into smaller nuclei, or it can combine with another nucleus or particle. Nuclear changes can happen only under certain circumstances. They happen without intervention in radioactive elements, scientists make them happen, with great difficulty, in a nuclear reactor, and they happen all the time in the cores of stars.
Radioactive Decay
Radioactive Decay
Recall that radioactive isotopes are unstable. By ejecting a particle, the nucleus of a radioactive atom can become stable. The process of ejecting or emitting pieces from the nucleus of an atom is called radioactive decay.
Scientists have identified the various subatomic particles, particles smaller than the atoms themselves, that are emitted from or shot out of the nucleus during radioactive events. These include alpha particles and beta particles.
Important to Know
Many elements have both stable and radioactive isotopes. For example, carbon-12 and carbon-13 are stable while carbon-14 is radioactive.
ALPHA DECAY
Alpha decay involves the ejection of an alpha particle from the nucleus of an atom. An alpha particle consists of two protons and two neutrons and can be represented by the Greek letter α, alpha. Because an alpha particle has two protons, it is the same as the nucleus of a helium atom.
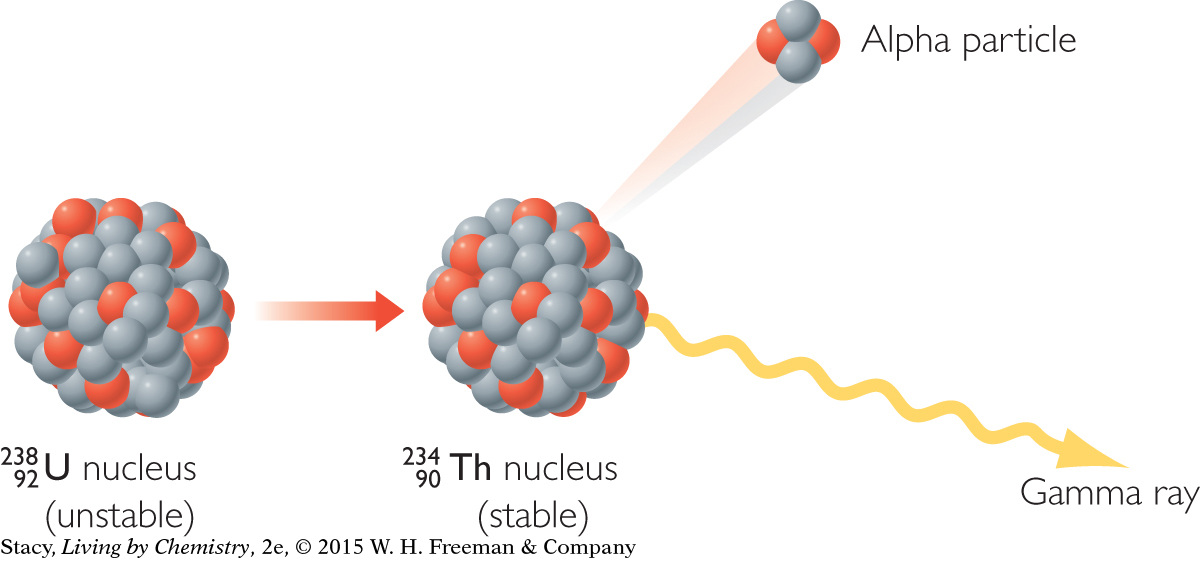
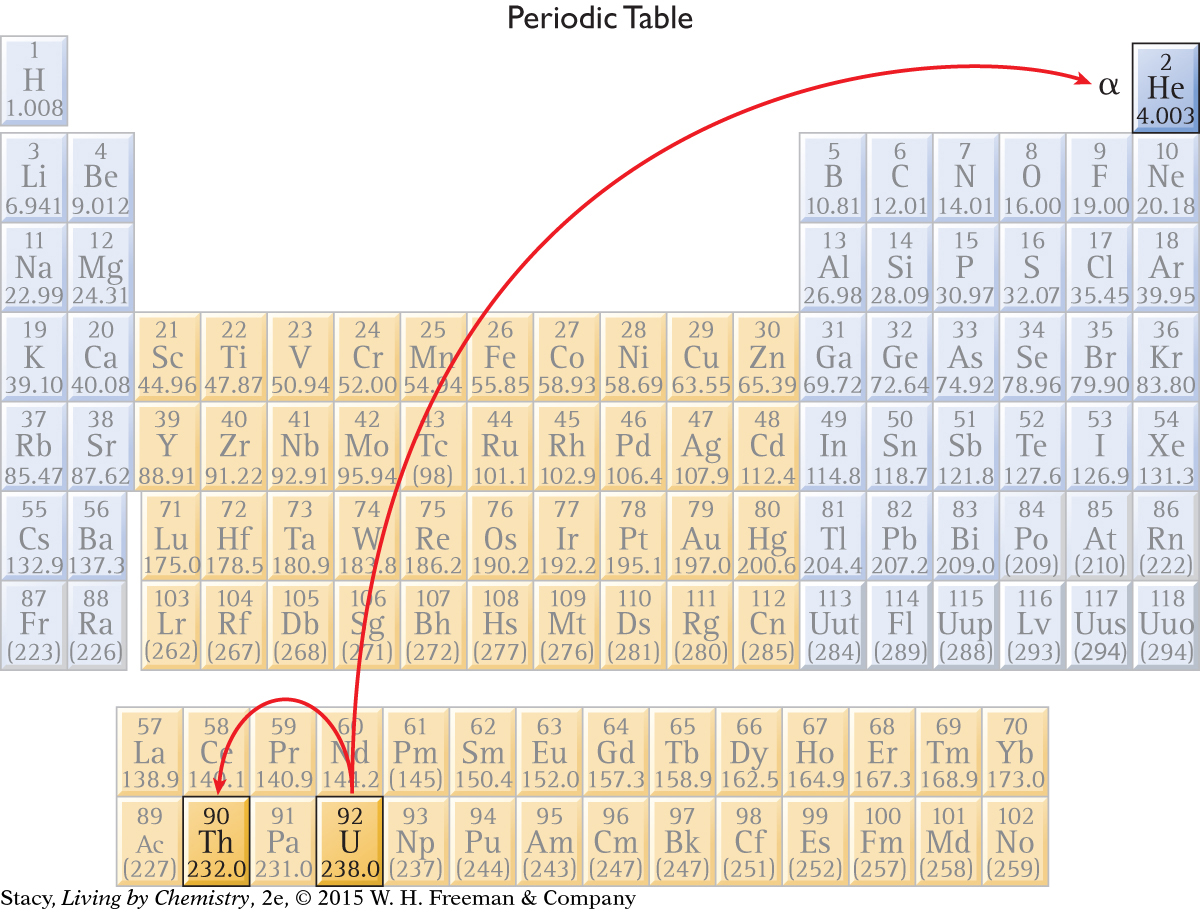
An alpha particle carries two protons away from the nucleus of an atom. This changes the identity of the element. So, when an atom of uranium, U, atomic number 92, undergoes alpha decay, an atom of thorium, Th, atomic number 90, is formed. This is why alpha decay causes you to move two spaces backward on the Nuclear Quest game board. Notice that a gamma ray is often released as a result of alpha decay.
HISTORY CONNECTION
HISTORY
CONNECTION
Marie Curie received the Nobel Prize for her groundbreaking work on radioactive substances. She was the first woman to win the prize, and she actually won two Nobel Prizes—one in Physics (1903) and one in Chemistry (1911). Like other pioneers, she was unaware of the dangers of radioactive samples and sometimes carried them around in her pockets, which probably cut short her life.

Big Idea
Big Idea
The elemental identity of an atom is determined by the number of protons it has.
BETA DECAY
Beta decay involves the ejection of an electron from the nucleus of an atom. The ejected electron is called a beta particle. Beta particles can be represented by the Greek letter β, beta. You may wonder how an electron got into the nucleus of an atom. In fact, electrons do not exist by themselves within the nucleus. However, in beta decay a neutron can split into two parts, becoming an electron and a proton. The electron is ejected and the proton stays behind in the nucleus.
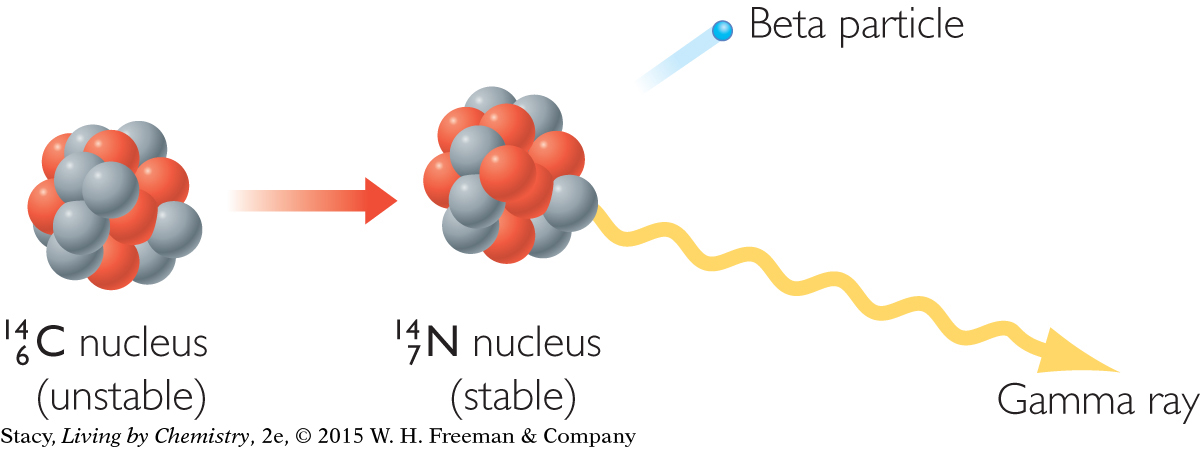
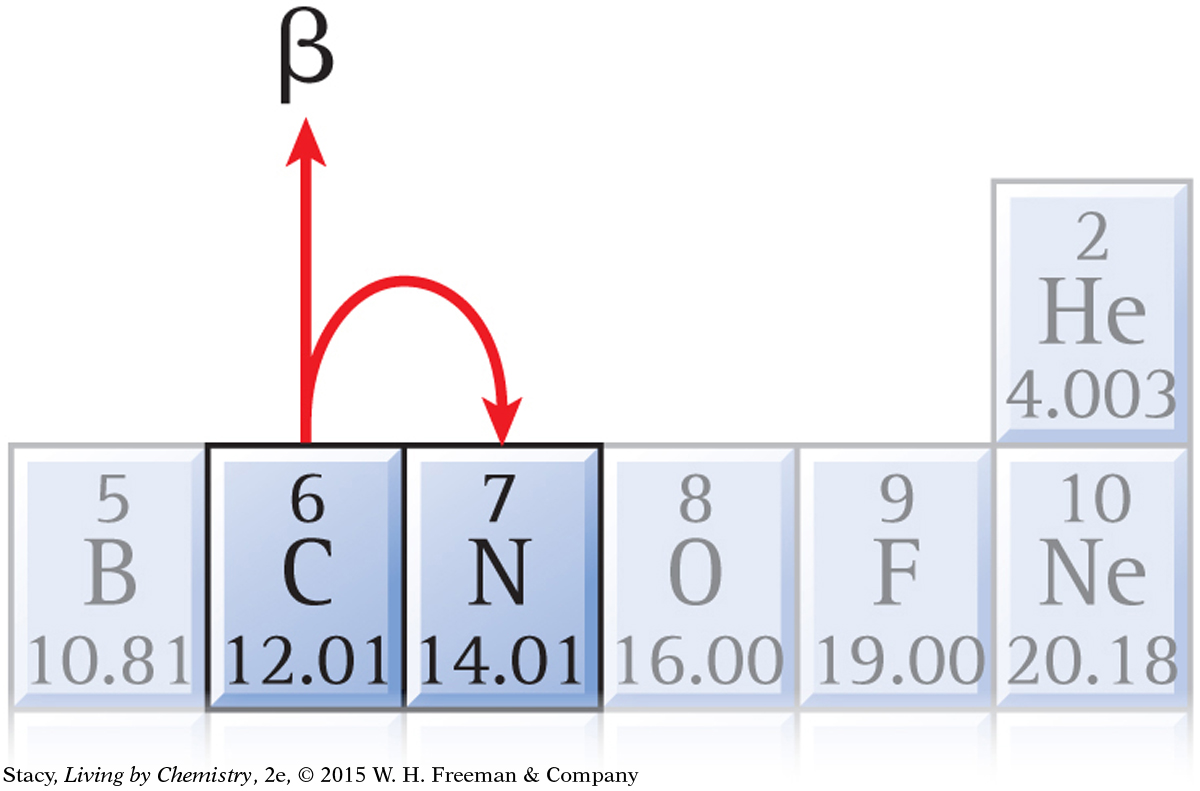
Removal of an electron from the nucleus of an atom through this unique process leaves that atom with one less neutron, one more proton, and a new identity. This is why beta decay causes you to move one space forward in the Nuclear Quest game. Beta decay can also result in the release of gamma rays.
Example
Plutonium-241
The radioactive isotope plutonium-241, 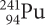 , decays by emitting a beta particle. What isotope is formed?
, decays by emitting a beta particle. What isotope is formed?
Solution
The atomic number of plutonium is 94, so it has 94 protons. In beta decay, a neutron becomes a proton. This increases the number of protons in the nucleus by one, but decreases the number of neutrons by one. The atomic mass stays the same because protons and neutrons have the same mass. The atomic number of the new atom is 95, and the new mass is still 241 amu. Element 95 is americium, Am.
The new isotope is americium-241.
HALF-LIFE
Carbon-14 has a half-life of 5730 years. This means that it will take 5730 years for half of a carbon-14 sample to decay to nitrogen-14. It will take another 5730 years for half of the remaining carbon-14 to decay, and so on. By measuring the remaining amount of carbon-14 compared to the amount of stable carbon, the age of the sample can be determined.
CAREER CONNECTION
CAREER
CONNECTION
Carbon-14 is a rare radioactive isotope of carbon that builds up to a steady level in living things as long as they are alive. When they die, the carbon-14 begins to decay at a predictable rate. Scientists have learned how to determine the age of a carbon fossil or artifact by measuring the amount of carbon-14 left in a sample. This process is called carbon dating.

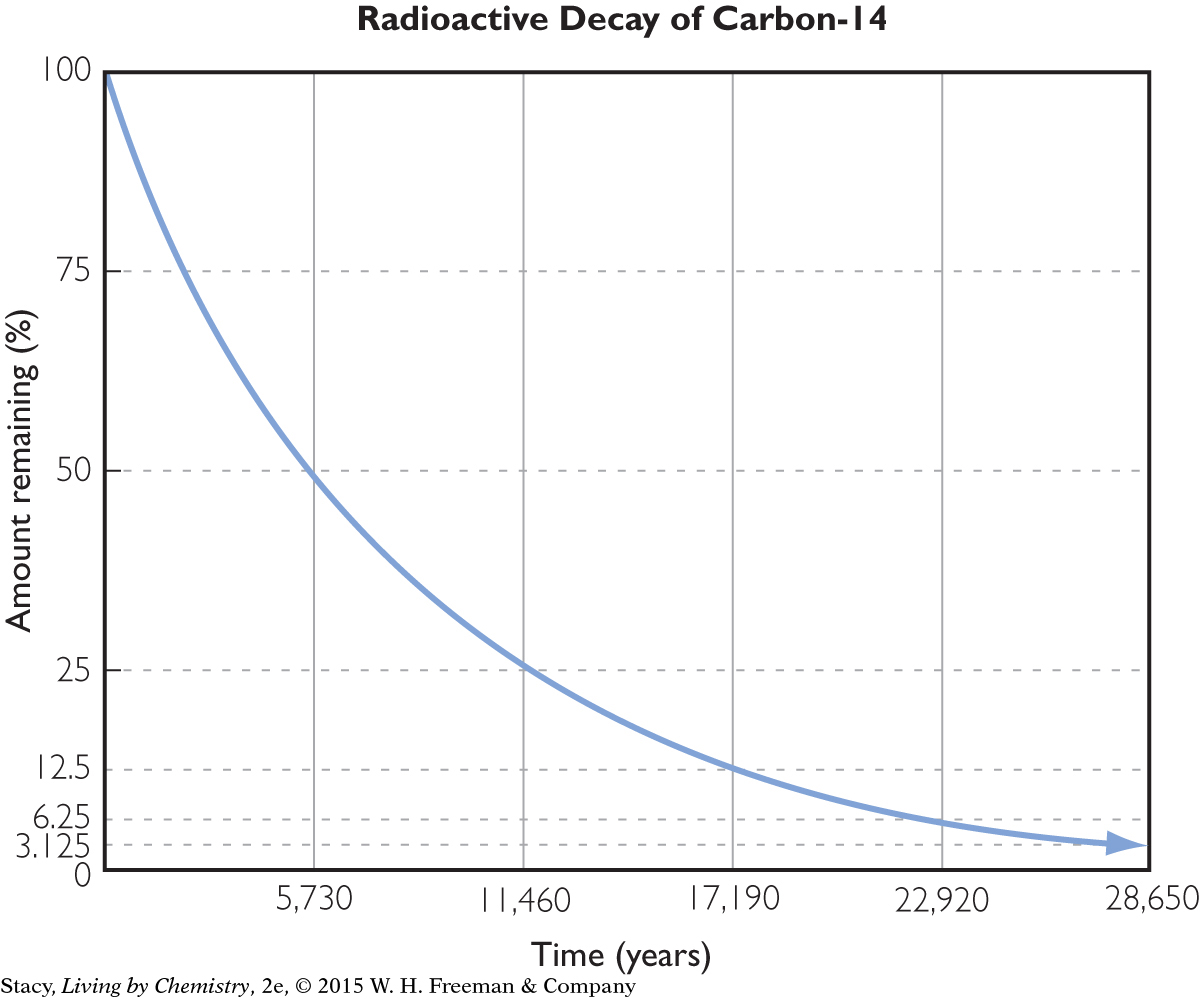
RADIATION
The particles and rays that are emitted during nuclear reactions are forms of radiation. So alpha and beta particles are both forms of radiation. Gamma rays are often emitted during radioactive events. Gamma rays are a kind of radiation similar to light, microwaves, and x-rays except they are much higher in energy, so they can be very dangerous. Gamma rays are represented by the Greek letter γ, gamma. When gamma rays are emitted, the identity of the emitting atom does not change.
Naturally occurring radiation does exist, with low levels coming from sources in the Earth, as well as from the Sun and beyond. Humans have learned how to use certain types of radiation for a variety of scientific purposes. However, radiation from nuclear reactions can be harmful to your health.
Even though radiation can be dangerous, it can also be used to help people. For example, some cancer patients receive radiation treatments to kill cancerous cells so that it kills those cells but doesn’t damage the rest of the body. Radiation can also be used to kill bacteria and viruses on food, particularly meat and vegetables. This helps reduce the risk of food poisoning.
Fission and Fusion
Fission and Fusion
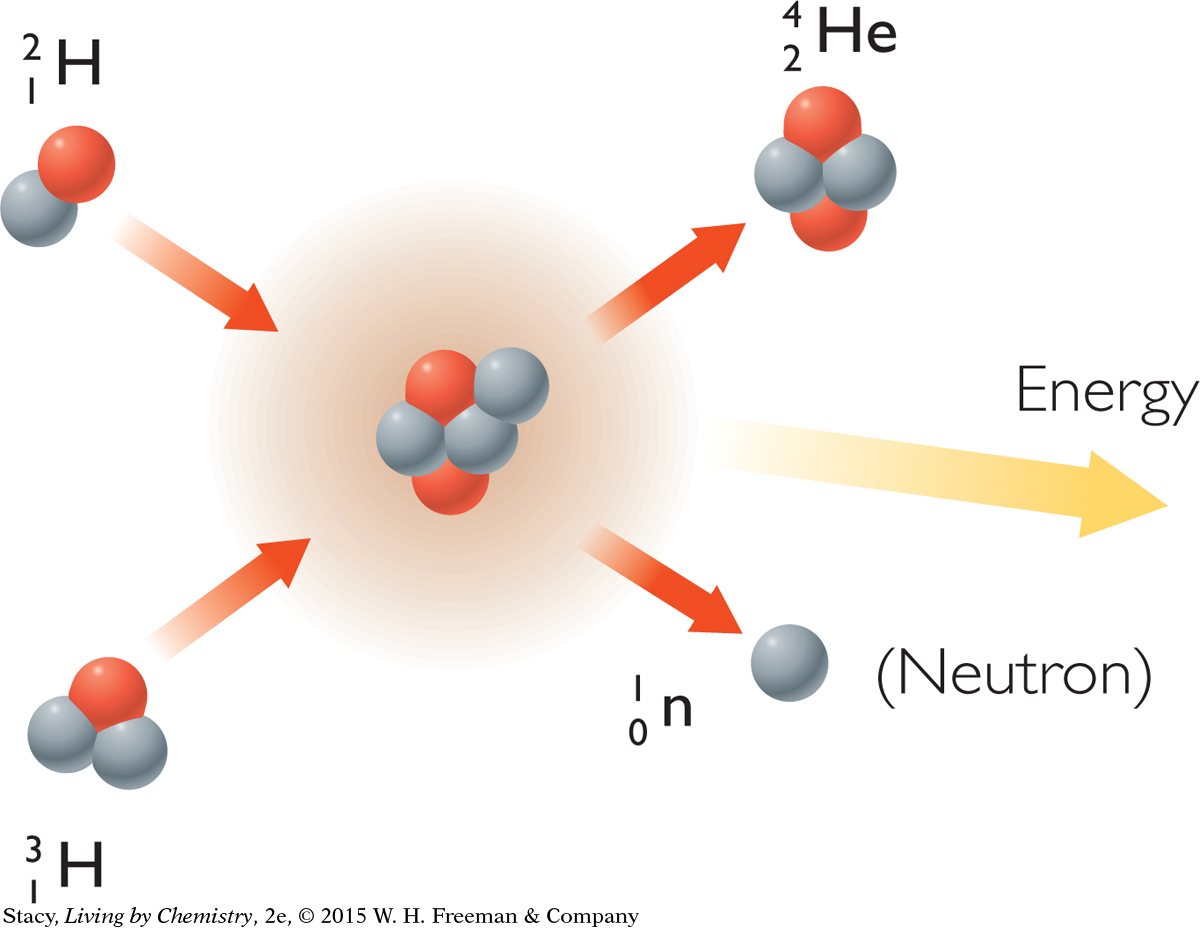
The splitting apart of a nucleus is called fission. The result is two atoms with smaller nuclei. Fission can occur spontaneously when the nucleus of an atom is unstable. Scientists can also make nuclear fission happen by shooting neutrons at a nucleus. Fission reactions are accompanied by radiation.
CAREER CONNECTION
CAREER
CONNECTION
X-rays are similar to gamma rays except that they are not generated by radioactive samples. Using quick exposures, doctors and dentists can image your bones. However, long-term exposure to radiation can lead to illness and even death. So when patients are having x-rays taken, they wear a lead shield to protect their organs and health professionals leave the room.

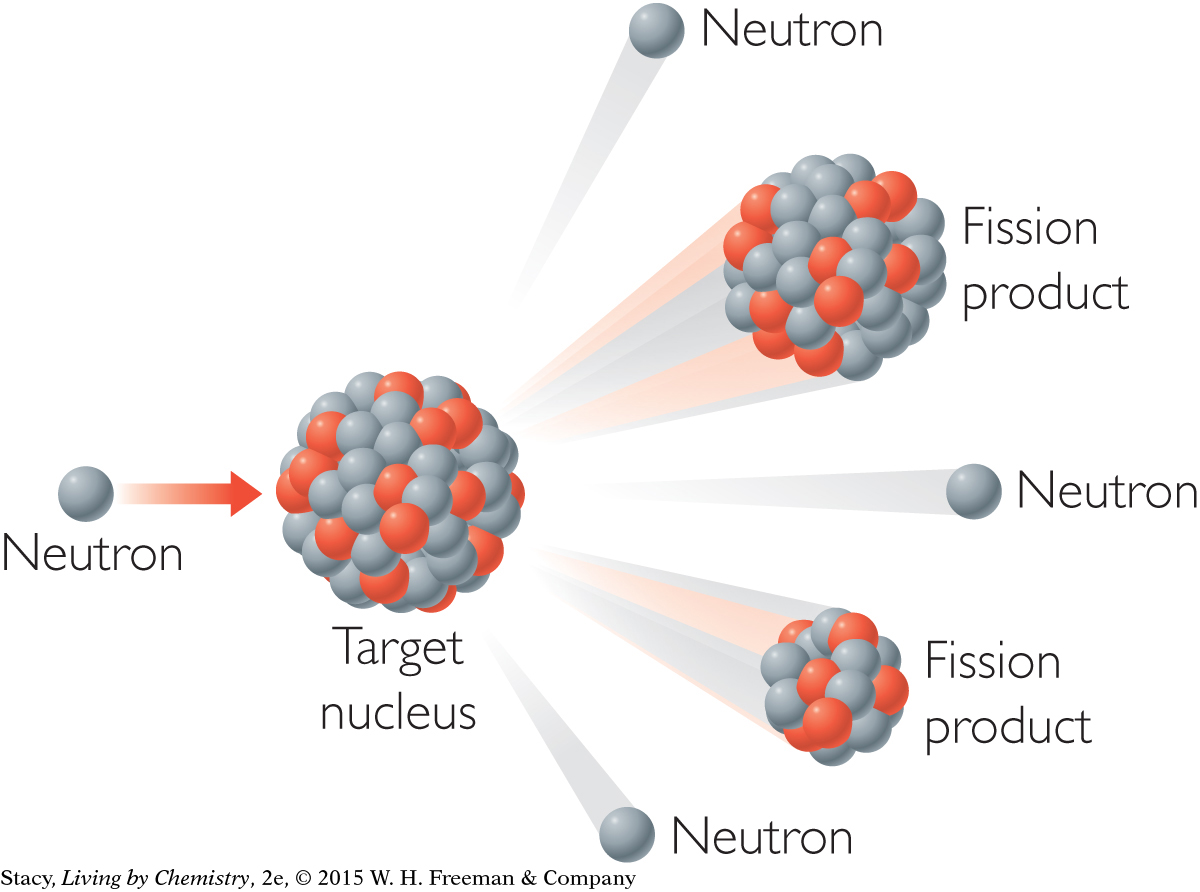
Another type of nuclear reaction is fusion. During fusion, nuclei join to form a larger nucleus, resulting in an atom of a different element. Temperatures of around 100,000,000 8C are required before nuclei can successfully fuse together. So the natural conditions on Earth do not support fusion.
LESSON SUMMARY
LESSON SUMMARY
What are nuclear reactions?
KEY TERMS
nuclear reaction
radioactive decay
alpha decay
alpha particle
beta decay
beta particle
half-life
radiation
gamma ray
fission
fusion
Radioactive decay, fission, and fusion are all forms of nuclear reactions. When radioactive decay is taking place, particles are emitted from the nucleus. Fission is the process by which the nucleus breaks into smaller nuclei. Fusion is the process by which nuclei combine to make a larger nucleus. Nuclear reactions can involve changes in atomic number, which mean changes in atomic identity. Radiation, such as the emission of alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays, accompanies decay and fission. All forms of radiation can cause harm to humans, but some forms are more damaging than others.
Exercises
Reading Questions
What is a nuclear reaction?
What is the difference between alpha decay and beta decay?
What type of radiation is most harmful to living things: alpha radiation, beta radiation, or gamma radiation? Why?
Reason and Apply
Explain why the mass of an atom changes when an alpha particle is emitted.
Explain why the mass number of an atom does not change when a beta particle is emitted.
An alpha particle is not a neutral atom. It has a charge of +2. Why is this the case?
Suppose each of these isotopes emits a beta particle. Give the isotope name and symbol for the isotope that is produced. Place a checkmark next to the symbol for isotopes that are stable. (Consult the isotope graph on page 66 of Lesson 14: Isotopia.)
potassium-42
iodine-131
iron-52
sodium-24
Suppose each of these isotopes emits an alpha particle. Give the isotope name and symbol for the isotope that is produced. Place a checkmark next to the isotopes produced that are stable. (Consult the isotope graph on page 66 of Lesson 14: Isotopia.)
platinum-175
gadolinium-149
americium-241
thorium-232
The following items were found at an ancient campsite: an ax with a stone blade and a wooden handle, a clay pot, ashes of a campfire, a jawbone of a deer, and an arrowhead. Which objects could be used to determine the age of the site? Explain.
Scientists determine that the wooden beams of a sunken ship have 67% of the concentration of carbon-14 that is found in the leaves of a tree alive today. Find the age of the ship and explain how you determined it. List three possible sources of error in your determination.
What fraction of the original
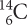 would be in a wooden ax handle that was 17,190 years old?
would be in a wooden ax handle that was 17,190 years old?Suppose
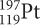 undergoes beta decay. The isotope that forms then also undergoes beta decay. What is the final product?
undergoes beta decay. The isotope that forms then also undergoes beta decay. What is the final product?