Comparative Drosophila Genomics
The fruit fly Drosophila melanogaster is one of the workhorses of genetics. Its genome, sequenced in 2000, was the second animal genome to be deciphered. In 2007, a consortium of 250 researchers from different parts of the world published the genome sequences of 10 additional species of Drosophila. Combined with the already sequenced genomes of D. melanogaster and D. pseudoobscura, this effort provided genomic data for 12 species of Drosophila, allowing detailed evolutionary analysis of this group of insects.
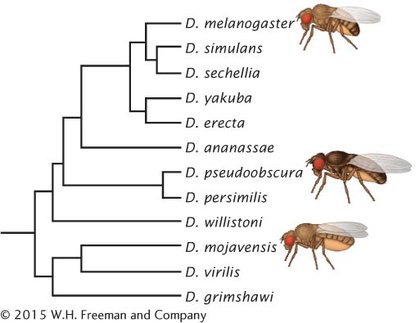
The 12 Drosophila species that were sequenced are found throughout the world, and all diverged from a common ancestor some 60 million years ago (Figure 15.10). Genome size in the group varies from 130 million base pairs in D. mojavensis to 364 million base pairs in D. virilis (Table 15.4). The number of protein-
| Species | Genome size (millions of base pairs) | Number of protein- |
|---|---|---|
| D. melanogaster | 200 | 13,733 |
| D. simulans | 162 | 15,983 |
| D. sechellia | 171 | 16,884 |
| D. yakuba | 190 | 16,423 |
| D. erecta | 135 | 15,324 |
| D. ananassae | 217 | 15,276 |
| D. pseudoobscura | 193 | 16,363 |
| D. persimilis | 193 | 17,325 |
| D. willistoni | 222 | 15,816 |
| D. virilis | 364 | 14,680 |
| D. mojavensis | 130 | 14,849 |
| D. grimshawi | 231 | 15,270 |
|
Source: Drosophila 12 Genome Consortium, Evolution of genes and genomes on the Drosophila phylogeny, Nature 450:203–218, 2007. |
||
Transposable elements have played an important role in the evolution of Drosophila genomes. The percentage of DNA that consists of the remnants of transposable elements ranges from 2.7% of the genome in D. simulans to 25% of the genome of D. ananassae. The amount of DNA contributed by transposable elements accounts for much of the difference in genome size among the species. Genomic rearrangements (inversions and translocations, see Chapter 6) were frequent in the evolution of this group. The rate of evolution varies among different classes of genes: genes controlling olfaction, immunity, and insecticide resistance have evolved at a faster rate than other genes.