Lethal Alleles
A lethal allele causes death at an early stage of development—
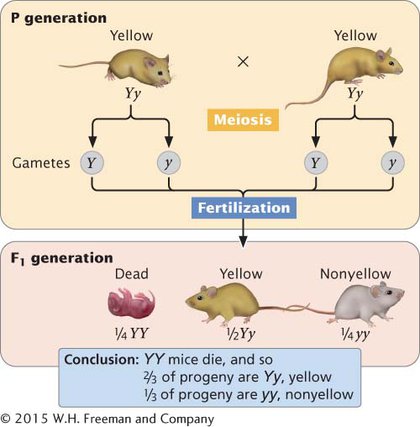
Another example of a lethal allele, originally described by Erwin Baur in 1907, is found in snapdragons. The aurea strain in these plants has yellow leaves. When two plants with yellow leaves are crossed, 2/3 of the progeny have yellow leaves and 1/3 have green leaves. When green is crossed with green, all the progeny have green leaves; when yellow is crossed with green, however, ½ of the progeny have green leaves and ½ have yellow leaves, confirming that all yellow-
In this example, like that of yellow coat color in mice, the lethal allele is recessive because it causes death only in homozygotes. Unlike its effect on survival, the effect of the allele on color is dominant; in both mice and snapdragons, a single copy of the allele in heterozygotes produces a yellow color. These examples illustrate the point made earlier that the type of dominance depends on the aspect of the phenotype examined.
Many lethal alleles in nature are recessive, but lethal alleles also can be dominant; in this case, homozygotes and heterozygotes for the allele die. Truly dominant lethal alleles cannot be transmitted unless they are expressed after the onset of reproduction.  TRY PROBLEM 29
TRY PROBLEM 29
CONCEPTS
A lethal allele causes death, frequently at an early developmental stage, so that one or more genotypes are missing from the progeny of a cross. Lethal alleles therefore modify the ratios of progeny resulting from a cross.