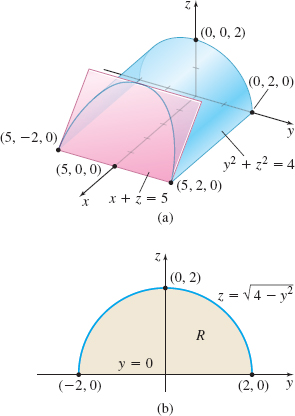
EXAMPLE 6Finding the Volume of a Solid That Is yz-simple
Find the volume V of the solid E that is enclosed by the cylinder y2+z2=4, and the planes x=0, z=0, and x+z=5.
Solution Figure 50(a) shows that the solid E is yz-simple. The front surface is the plane x2(y,z)=5−z and the back surface is the plane x1(y,z)=0. The region R in the yz-plane is enclosed by the y-axis and the semi-circle z=√4−y2; it is y-simple. So, 0≤z≤√4−y2 and −2≤y≤2. See Figure 50(b). The volume V of E is given by V=∭