EXAMPLE 2Finding a Triple Integral Using Cylindrical Coordinates
Give a geometric interpretation of the triple integral ∫1−1∫√1−x2−√1−x2∫2√1−x2−y20dzdydx
Then use cylindrical coordinates to find the triple integral.
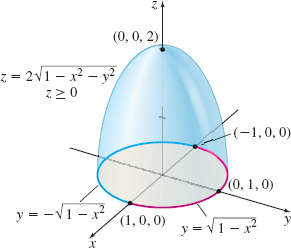
Solution The solid E of integration and its projection onto the xy-plane can be described by the inequalities 0≤z≤2√1−x2−y2−√1−x2≤y≤√1−x2−1≤x≤1
The limits of integration on z are z=0 and z=2√1−x2−y2=√4−4x2−4y2 or, equivalently, z2=4−4x2−4y2, z≥0. We can interpret the integral as the volume of a solid E that is the upper half of the ellipsoid 4x2+4y2+z2=4, z≥0, as shown in Figure 55. From the x and y limits of integration, the projection onto the xy-plane is the region R enclosed by the circle x2+y2=1.
To find the integral, we convert the rectangular coordinates to cylindrical coordinates. Then z=2√1−x2−y2=2√1−(x2+y2)=2√1−r2
The projection onto the xy-plane is the region enclosed by the circle x2+y2=1. So in cylindrical coordinates, we have 0≤z≤2√1−r20≤r≤10≤θ≤2π
Then ∫1−1∫√1−x2−√1−x2∫2√1−x2−y20dzdydx=∫2π0∫10∫2√1−r20dzrdrdθ=∫2π0∫10[z]2√1−r20rdrdθ=∫2π0∫102r√1−r2 drdθ=∫2π0[−23(1−r2)3/2]10dθ=23∫2π0dθ=4π3
953
The value of the triple integral 4π3 equals the volume V of the solid. That is, V=4π3 cubic units