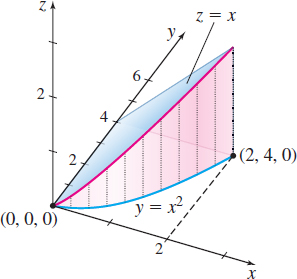
EXAMPLE 4Finding the Lateral Surface Area of a Cylinder
Find the lateral surface area A of the cylinder that lies above the xy-plane, below the surface z=f(x,y)=x, and formed by lines parallel to the z -axis that intersect the curve y=x2, 0≤x≤2.
Solution Figure 17 illustrates the cylinder. Along C, y=x2, the differential ds of arc length is ds=√1+(dydx)2dx=↑dydx=2x√1+4x2dx
The lateral surface area A of the cylinder is A=∫Cf(x,y)ds=∫Cxds=∫20x√1+4x2dxLet u=1+4x2; then du=8xdx or xdx=18du.When x=0, u=1; when x=2, u=17.=∫17118√udu=[14u3/23]171=17√17−112