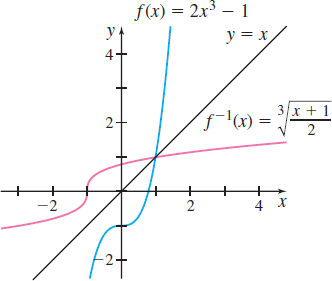
EXAMPLE 5Finding the Inverse Function
The function f(x)=2x3−1 is one-to-one. Find its inverse.
Solution We follow the steps given above.
Step 1 Write f as y=2x3−1.
Step 2 Interchange the variables x and y. x=2y3−1
This equation defines f−1 implicitly.
Step 3 Solve the implicit form of the inverse function for y. x+1=2y3y3=x+12y=3√x+12=f−1(x)
Step 4 Check the result. f−1(f(x))=f−1(2x3−1)=3√(2x3−1)+12=3√2x32=3√x3=xf(f−1(x))=f(3√x+12)=2(3√x+12)3−1=2(x+12)−1=x+1−1=x