EXAMPLE 6Using the Law of the Sines to Solve a Triangle
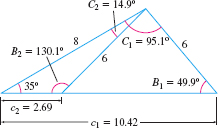
Solve the triangle with side a=6, side b=8, and angle A=35∘, which is opposite side a.
Solution Because two sides and an opposite angle are known (SSA), we use the Law of Sines to find angle B. sinAa=sinBb
Since a=6, b=8, and A=35∘, we have sin35∘6=sinB8
A-37
sinB=8sin35∘6≈0.765 B1≈49.9∘orB2≈180∘−49.9∘=130.1∘
For both choices of B, we have A+B<180∘. So, there are two triangles, one containing the angle B1≈49.9∘ and the other containing the angle B2≈130.1∘. The third angle C is either C1=180∘−A−B1≈↑A=35∘B1=49.9∘95.1∘orC2=180∘−A−B≈↑A=35∘B2=130.1∘14.9∘
The third side c satisfies the Law of Sines, so sinAa=sinC1c1sinAa=sinC2c2sin35∘6=sin95.1∘c1sin35∘6=sin14.9∘c2c1=6sin95.1∘sin35∘≈10.42c2=6sin14.9∘sin35∘≈2.69 The two solved triangles are illustrated in Figure 63.