EXAMPLE 6Snell’s Law of Refraction
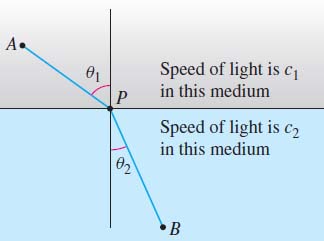
Light travels at different speeds in different media (air, water, glass, etc.) Suppose that light travels from a point A in one medium, where its speed is c1, to a point B in another medium, where its speed is c2. See Figure 61. We use Fermat’s principle that light always travels along the path that requires the least time to prove Snell’s Law of Refraction. \bbox[5px, border:1px solid black, #F9F7ED]{\bbox[#FAF8ED,5pt]{\frac{{\sin {\theta _1}}}{{{c_1}}} = \frac{{\sin {\theta _2}}}{{{c_2}}}}}
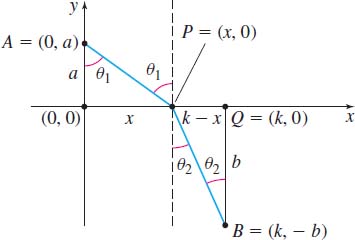
Solution We position the coordinate system, as illustrated in Figure 62. The light passes from one medium to the other at the point P. Since the shortest distance between two points is a line, the path taken by the light is made up of two line segments—from A=( 0,a) to P=( x,0) and from P=( x,0) to B=(k,-b), where a, b, and k are positive constants.
Since \hbox{Time}= \dfrac{{\rm Distance}}{{\rm Speed }}
the travel time t_{1} from A=( 0,a) to P=( x,0) is t_{1}=\frac{\sqrt{x^{2}+a^{2}}}{c_{1}}
and the travel time t_{2} from P=( x,0) to B=( k,-b) is t_{2}=\frac{\sqrt{(k-x)^{2}+b^{2}}}{c_{2}}
The total time T=T(x) is given by T(x) =t_{1}+t_{2}=\frac{\sqrt{x^{2}+a^{2}}}{c_{1}}+\frac{\sqrt{({k-x})^{2}+b^{2}}}{c_{2}}
To find the least time, we find the critical numbers of T. \begin{equation} T' (x) =\frac{x}{c_{1}\sqrt{x^{2}+a^{2}}}-\frac{k-x}{c_{2} \sqrt{({k-x})^{2}+b^{2}}}=0 \tag{1} \end{equation}
From Figure 62, \begin{equation} {\frac{x}{\sqrt{x^{2}+a^{2}}}=\sin\, \theta _{1}}\qquad \hbox{and}\qquad { \frac{k-x}{\sqrt{({k-x})^{2}+b^{2}}}=\sin\, \theta _{2}} \tag{2} \end{equation}
Using the result from (2) in equation (1), we have \begin{eqnarray*} T' (x) = \frac{\sin\, \theta _{1}}{c_{1}}-{\frac{\sin\, \theta _{2}}{c_{2}}} &=&0 \\[3pt] {\frac{\sin\, \theta _{1}}{c_{1}}} &=&{\frac{\sin\, \theta _{2}}{c_{2}}} \end{eqnarray*}
325
Now to ensure that the minimum value of T occurs when T' (x)=0, we show that T'' (x) >0. From (1), \begin{eqnarray*} {T'' }(x) &=&{\frac{d}{dx}\left[ {\frac{x}{c_{1}\sqrt{ x^{2}+a^{2}}}}\right] -\frac{d}{dx}\left[ {\frac{k-x}{c_{2}\sqrt{({k-x} )^{2}+b^{2}}}}\right] } \\[3pt] &=&{\frac{a^{2}}{c_{1}({x^{2}+a^{2}})^{3/2}}+\frac{b^{2} }{c_{2}[{({k-x})^{2}+b^{2}}]^{3/2}}>0} \end{eqnarray*}
Since T'' (x) >0 for all x, T is concave up for all x, and the minimum value of T occurs at the critical number. That is, T is a minimum when \dfrac{\sin\, \theta _{1}}{c_{1}}=\dfrac{\sin\, \theta _{2}}{c_{2}}.