13.3 Assess Your UnderstandingPrinted Page 888
Concepts and Vocabulary
Multiple Choice Suppose z=f(x,y) is a function with domain D, and (x0,y0) is an interior point of D. If f(x0,y0)≥f(x,y) for all points (x,y) within some disk centered at (x0,y0), then f has [(a) a local maximum, (b) a local minimum, (c) a saddle point, (d) none of these] at (x0,y0).
(a)
If z=f(x,y) is a function of two variables whose domain is an open set D containing the point (x0,y0), then the point (x0,y0) is a critical point of f if ________ or if fx(x0,y0) or fy(x0,y0) does not exist.
fx(x,y)=fy(x,y)=0.
True or False It is possible for a function z= f(x,y) to have a local extremum at a point (x0,y0) that is not a critical point.
False
Multiple Choice If fx(x0,y0)=0 and fy(x0,y0)=0, but f does not have a local extremum at (x0,y0), then the point (x0,y0,f(x0,y0)) is called [(a) a local maximum value, (b) a local minimum value, (c) a saddle point, (d) none of these].
(c)
True or False The Extreme Value Theorem for Functions of Two Variables guarantees that a function z=f(x,y) of two variables, that is continuous on a closed, bounded set D, has an absolute maximum and an absolute minimum on D.
True
If z=f(x,y) is a function of two variables that is continuous on a closed, bounded set D, then the absolute extrema are either at the critical points of f in D or on the ________ of D.
boundary
Skill Building
In Problems 7–12, find all the critical points for each function.
f(x,y)=x4−2x2+y2+5
The critical points are (0,0),(1,0), and (−1,0).
f(x,y)=x2−y2+6x−2y+4
f(x,y)=4xy−x4−y4+2
The critical points are (0,0),(1,1), and (−1,−1).
f(x,y)=x3+6xy+3y2+3
f(x,y)=e−x(x2+y)
There are no critical points.
f(x,y)=xy+2x+4y
In Problems 13–32, find the local maxima, local minima, and saddle points, if any, for each function.
z=x2+y2−2x+4y+2
There is a local minimum at (1,−2); the local minimum value is z=−3.
z=x2+y2−4x+2y−4
z=x2+4y2−4x+8y−1
There is a local minimum at (2,−1); the local minimum value is z=−9.
z=2x2−y2+4x−4y+8
z=x3−6xy+y3
The point (0,0,0) is a saddle point of z. There is a local minimum at (2,2); the local minimum value is z=−8.
z=x2−3xy−y2
z=x2+3xy−y2+4y−6x
The point (0,2,4) is a saddle point of z.
z=2x2+xy+y2−2x+3y+6
z=x3+3xy+y3
The point (0,0,0) is a saddle point of z. There is a local maximum at (−1,−1); the local maximum value is z=1.
z=x3−3xy−y3
z=x3+x2y+y2
The points (3,−4.5,6.75) and (0,0,0) are saddle points of z.
z=3y3−x2y+x
889
z=yx+y
There are no critical points.
z=xx+y
z=cosx+cosy
The function has critical points at (x,y)=(mπ,nπ) for integers m and n. For odd values of m and n, the function has a local minimum; the local minimum value is z=−2. For even values of m and n, the function has a local maximum; the local maximum value is z=2. For odd m and even n OR even m and odd n, (mπ,nπ,0) is a saddle point of z.
z=x2+4−4xcosy
z=y2−6ycosx+6
For integer n, the function has a local minimum at (2πn,3) and (π+2πn,−3); the local minimum value is −3. For integer n, the points (π2+2πn,0,6) and (−π2+2πn,0,6) are saddle points of z.
z=x2−6xsiny+2
z=exy
The point (0,0,1) is a saddle point of z.
z=xye−(x+y)
In Problems 33–38, find the absolute maximum and absolute minimum of f on the domain D.
z=f(x,y)=x2−4xy+4y;D: 0≤x≤2, 0≤y≤1
The absolute maximum value of f is 4; the absolute minimum value of f is 0.
z=f(x,y)=x2−4xy+4y;D: 0≤x≤3, 0≤y≤2
z=f(x,y)=x2+2x+y2−2y;D: x2+y2≤4
The absolute maximum value of f is 4+4√2; the absolute minimum value of f is −2.
z=f(x,y)=x2−4x+y2−4y;D: x2+y2≤9
z=f(x,y)=xy+4x−3y+5;D: the closed triangular region whose vertices are (0,0),(0,4), and (5,4)
The absolute maximum value of f is 33; the absolute minimum value of f is −7.
z=f(x,y)=3xy−3x−6y+1;D: the closed triangular region whose vertices are (0,0),(5,0), and (0,3)
Applications and Extensions
Find the local extrema and saddle points, if any, of f(x,y)=sinxsiny.
For integers m and n, there are local minima at (−π2+2πm,π2+2πn) and (π2+2πm,−π2+2πn); the local minimum value is −1. For integers m and n, there are local maxima at (−π2+2πm,−π2+2πn) and (π2+2πm,π2+2πn); the local maximum value is 1. For integers m and n, (x,y,z)=(πm,πn,0) are saddle points of z.
Find the highest point of the paraboloid x2+y2−6x+4y+z+12=0 as follows:
- (a) Find the vertex of the paraboloid without using calculus.
- (b) Express z as a function of x and y and use calculus to find its maximum value. See the figure.
Geography The surface of a mountain is modeled by the graph of the function z=2xy−2x2−y2−8x+6y+4 where z is the height in kilometers. See the figure. If sea level is the xy-plane, how high is the mountain above sea level?
At its highest peak, the mountain is 14 km above sea level.
Geometry
- (a) Find the point on the plane 3x+2y+z=14 that is nearest the origin.
- (b) What is the distance of the point found in (a) from the origin?
Constructing a Box A rectangular box open at the top has a fixed surface area S. Find the dimensions that make its volume a maximum. Express the length, width, and depth of the box in terms of S.
The volume is a maximum when the length and width are √S3 and the depth is 12√S3.
Constructing a Box Rework Problem 43 if the box is closed.
Constructing a Box Rework Example 7 if the box is closed.
The dimensions of the closed box of volume V=500 cm3 that uses the least amount of material occur when the length, width, and depth are all 3√500 cm.
Minimizing Cost Find the dimensions of an open rectangular box having a volume of 80 cubic meters if the cost per square meter of the material to be used is $4 for the bottom, $3 for one of the sides, and $2 for the three remaining sides, and the total cost is to be minimized.
Standard Post Regulations The U.S. Postal Service regulations state that individual packages can be up to 130 in. in combined length and girth (the perimeter of a cross section at the widest spot) before additional charges apply.
- (a) Find the dimensions of maximum volume of a rectangular box that can be sent without additional charges.
- (b) Find the dimensions of maximum volume if the package is cylindrical.
Source: U.S. Postal Service, October, 2013, https://www.usps.com/standardpost.htm.
- (a) The rectangular box with maximum volume has a cross section of dimensions 653 inches by 653 inches and a length of 1303 inches.
- (b) The cylindrical box with maximum volume has a radius of 1303π inches and a length of 1303 inches.
Pharmacology A patient's reaction to an injection of x units of a certain drug, t hours after the injection, is given by y=x2(a−x)te−t0≤x≤a0≤t
where a>0 is a constant. Find the values of x and t, if any, that will maximize y.
Pharmacology Two drugs A and B are used simultaneously to treat a disease. A patient's reaction R to x units of Drug A and y units of Drug B is R(x,y)=x2y2(a−x)(b−y)0≤x≤a0≤y≤b
- (a) For a fixed amount x of Drug A, what amount y of Drug B produces the maximum reaction?
- (b) For a fixed amount y of Drug B, what amount x of Drug A produces the maximum reaction?
- (c) If amounts x and y are both variable, what amount of each maximizes the reaction?
- (a) For a fixed amount x of Drug A, y=2b3 units of Drug B produces the maximum reaction.
- (b) For a fixed amount y of Drug B, x=2a3 units of Drug A produces the maximum reaction.
- (c) Reaction is a maximum when x=2a3 units of Drug A and y=2b3 units of Drug B are used.
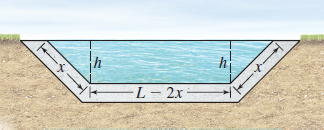
Agriculture An open irrigation channel is to be made into a symmetric form with three straight sides, as indicated in the figure.
- (a) If the total length of the three sides is L, find a channel design that will allow the maximum possible flow.
- (b) Is this design preferable to an open semicircular channel? Give the reasons why.
Fuel Cost See the figure. A fuel reservoir at D is planned to service plants located at A,B, and C. The cost, in thousands of dollars, of connecting the plants to D is determined by the formula F=6x2+6y2−4x−6y+5
Find the location of D that will minimize this cost.
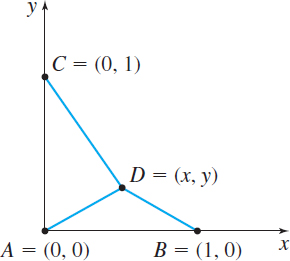
The location (13,12) will minimize the cost of connecting the plants to D.
890
Minimizing Cost The cost of material for the sides of a rectangular shipping container is a cents per square foot; the cost of the top and bottom material is 32a cents per square foot. If the volume is to be 32 cubic feet, what dimensions of the container will minimize its cost?
Metal Detector A metal detector is used to locate an underground pipe. When several meter readings of the detector are compared, the reading at an arbitrary point (x,y), where x≥0 and y≥0, is modeled by M=y(x−x2)−y2
Find the point (x,y) with the highest reading.
The location with the highest reading is (x,y)=(12,18).
Maximizing Profit A steel manufacturer produces two grades of steel, x kilograms of Grade A and y kilograms of Grade B. The cost C and revenue R in dollars are given by C=120x2+700x+y2−150y−12xyR=2700x−320x2+1000y−y2+12xy+10,000
If P= Profit =R−C, find the production (in kilograms) of Grades A and B that maximizes the manufacturer's profit.
Economics The demand functions for two products are p=12−x and q=8−y, where p and q are the respective prices (in thousands of dollars) of each product, and x and y are the respective amounts (in thousands of units) of each product sold. If the joint cost function is C(x,y)=x2+2xy+3y2
find the quantities x and y and the prices p and q that maximize profit. What is the maximum profit?
Production is maximized when x=207≈2.857 thousand units are sold at a price of p=647≈9.143 thousand dollars and y=27≈0.286 thousand units are sold at a price of q=547≈7.714 thousand dollars. The maximum profit is $18,286.
Economics The labor cost of a firm is modeled by the function Q(x,y)=x2+y2−xy−3x−6y−5
where x is the number of workdays required by a skilled worker and y is the number of workdays required by a semiskilled worker. Find the values of x and y for which the labor cost is a minimum.
Second Partial Derivative Test Suppose g(x,y)=Ax2+2Bxy+Cy2
where A, B, and C are constants. Show that:
- (a) If AC−B2>0, A≠0, then g(x,y) has a maximum at (0,0) if A<0 and a minimum at (0,0) if A>0.
- (b) If AC−B2<0, then g(x,y) has both positive and negative values at points (x,y) near (0,0), and (0,0,0) is a saddle point for z=g(x,y).
See Student Solutions Manual.
Challenge Problems
Find the distance between the skew lines L1: x=t−6, y=t, z=2t and L2: x=t, y=t, z=−t.
Method of Least Squares A scientist plots the points (x1,y1),…,(xn,yn) from her experimental data. Her theory tells her that the points should lie on a straight line, but they do not; perhaps as a result of experimental error. She is looking for the line y=mx+b that “best” fits the data. The most often used criterion is the least-squares fit, in which m and b are chosen to minimize n∑k=1(mxk+b−yk)2
- (a) Show that the minimizing values of m and b are m=nn∑k=1xkyk−n∑k=1xkn∑k=1yknn∑k=1x2k−(n∑k=1xk)2b=1n(n∑k=1yk−mn∑k=1xk)
- (b) Find the least-squares estimate y=mx+b for the points (0,2),(1,1),(2,2),(3,4), and (4,4). Plot the points and draw the line.
- (a) See Student Solutions Manual.
- (b) The equation of the least squares estimate is y=0.7x+1.2.
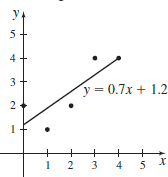
Let z=f(x,y) have continuous second-order partial derivatives. If u=u1i+u2j is a unit vector, there is a directional derivative Duf(x,y)=g(x,y). If g(x,y) is differentiable and if v=v1i+v2j is a unit vector, then Dvg(x,y)=u1v1fxx+(u1v2+u2v1)fxy+u2v2fyy. If we let A=fxx(x0,y0), B=fxy(x0,y0), and C=fyy(x0,y0), then we have an expression in the components u1 and u2 of u, and v1 and v2 of v. (See Section 13.1, Problem 77.)
- (a) In particular, if u=v, show that the second-order directional derivative at (x0,y0) is given by Au21+2Bu1u2+Cu22.
- (b) Let fx(x0,y0)=0=fy(x0,y0). Show that if A>0 and AC−B2>0, then z=f(x,y) has a local minimum at (x0,y0); if A<0 and AC−B2>0, then z=f(x,y) has a local maximum at (x0,y0); and if AC−B2<0, then z=f(x,y) has a saddle point at (x0,y0).
- (c) Show by examples that if AC−B2=0, we may have any of the above three possibilities.
