39.3 A Ribosome Is a Ribonucleoprotein Particle Made of Two Subunits
We now turn to ribosomes, the molecular machines that coordinate the interplay of aminoacyl-
A ribosome can be dissociated into a large subunit (50S) and a small subunit (30S) (Figure 39.7). These subunits can be further dissociated into their constituent proteins and RNAs. The small subunit contains 21 different proteins (referred to as S1 through S21) and a 16S RNA molecule. The large subunit contains 34 different proteins (L1 through L34) and two RNA molecules, a 23S and a 5S species.
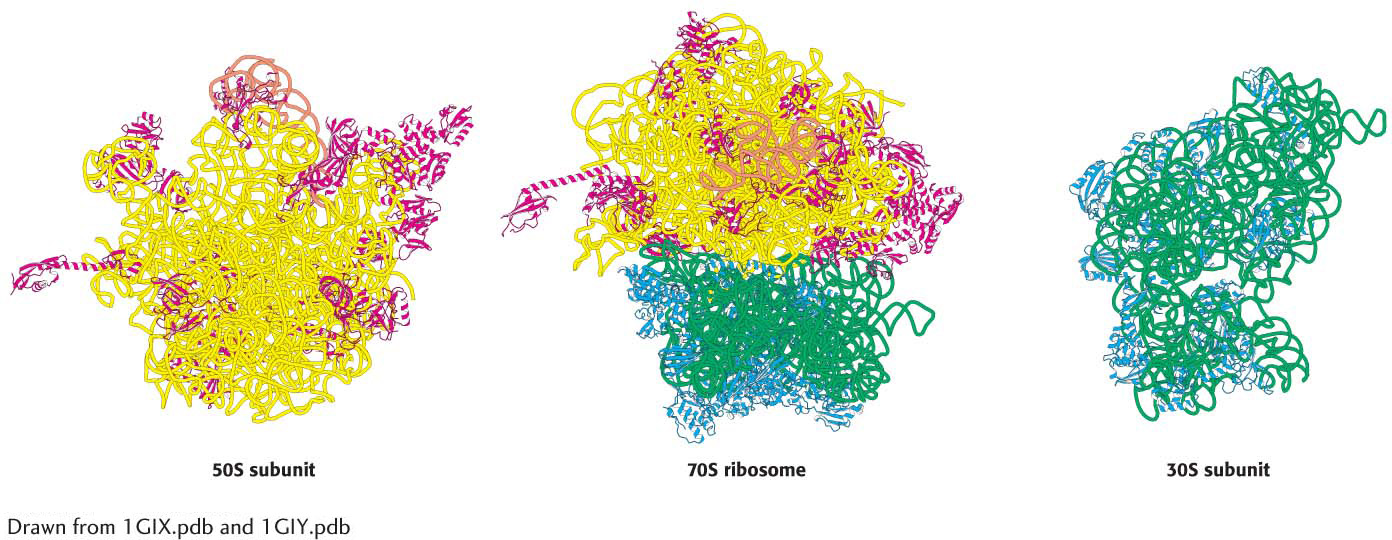
 Figure 39.7 The ribosome at high resolution. Detailed models of the ribosome based on the results of x-
Figure 39.7 The ribosome at high resolution. Detailed models of the ribosome based on the results of x-Ribosomal RNAs Play a Central Role in Protein Synthesis
The prefix ribo in the name ribosome is apt, because RNA constitutes nearly two-

For many years, the protein components of ribosomes were thought to orchestrate protein synthesis, with the RNA components serving primarily as structural scaffolding. But this idea raised a perplexing evolutionary “chicken-
Messenger RNA Is Translated in the 5′-to-3′ Direction
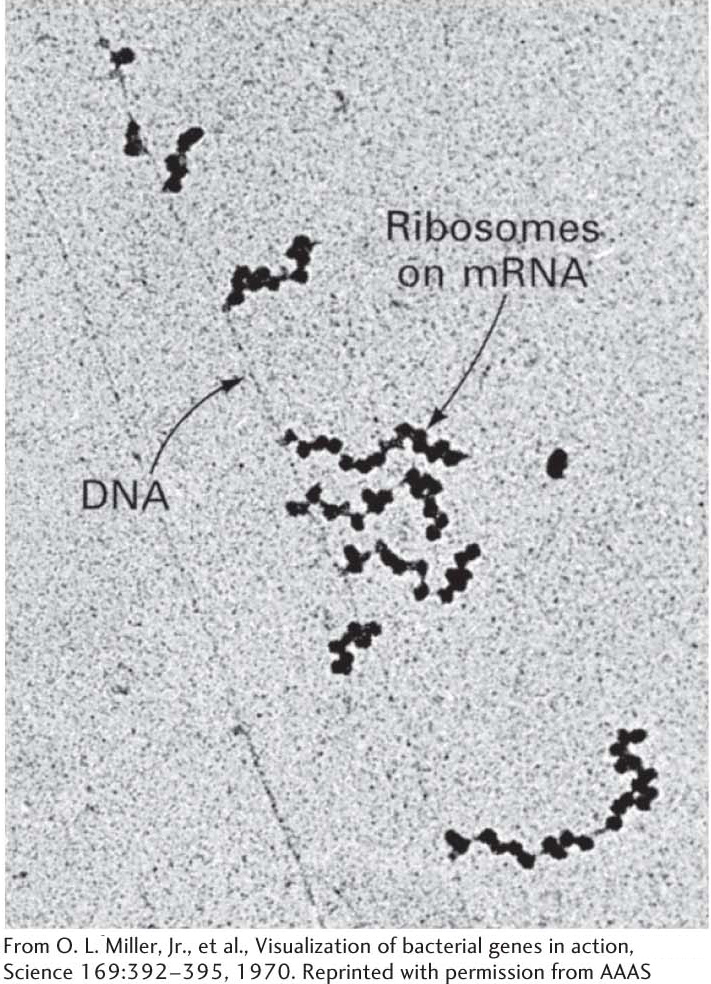
The sequence of amino acids in a protein is translated from the nucleotide sequence in mRNA, and the direction of translation is 5′ → 3′. The direction of translation has significant consequences. Recall that transcription also is in the 5′ → 3′ direction. If the direction of translation were opposite that of transcription, only fully synthesized mRNA could be translated. In contrast, because the directions are the same, mRNA can be translated while it is being synthesized. In bacteria, almost no time is lost between transcription and translation. The 5′ end of mRNA interacts with ribosomes very soon after it is made, much before the 3′ end of the mRNA molecule is finished. A key feature of bacterial gene expression is that translation and transcription are closely coupled in space and time. Many ribosomes can be translating an mRNA molecule simultaneously. This parallel synthesis markedly increases the efficiency of mRNA translation. The group of ribosomes bound to an mRNA molecule is called a polyribosome or a polysome (Figure 39.9).