PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 16.1
Gross versus net. The gross yield of ATP from the metabolism of glucose to two molecules of pyruvate is four molecules of ATP. However, the net yield is only two molecules of ATP. Why are the gross and net values different?
Question 16.2
Go together like the owl and the pussycat. Match each term with its description.
|
(a) Hexokinase _______ |
1. Forms fructose 1,6- |
|
(b) Phosphoglucose isomerase _______ |
2. Generates the first high- |
|
(c) Phosphofructokinase _______ |
3. Converts glucose 6- |
|
(d) Aldolase _______ |
4. Phosphorylates glucose |
|
(e) Triose phosphate isomerase _______ |
5. Generates the second molecule of ATP |
|
(f) Glyceraldehyde 3- |
6. Cleaves fructose 1, 6- |
|
(g) Phosphoglycerate kinase _______ |
7. Generates the second high- |
|
(h) Phosphoglycerate mutase _______ |
8. Catalyzes the interconversion of three- |
|
(i) Enolase _______ |
9. Converts 3- |
|
(j) Pyruvate kinase _______ |
10. Generates the first molecule of ATP |
Question 16.3
Who takes? Who gives? Lactic acid fermentation and alcoholic fermentation are oxidation–
Question 16.4
ATP yield. Each of the following molecules is processed by glycolysis to lactate. How much ATP is generated from each molecule?
Glucose 6-
phosphate Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Glyceraldehyde 3-
phosphate Fructose
Sucrose
Question 16.5
Enzyme redundancy? Why is it advantageous for the liver to have both hexokinase and glucokinase to phosphorylate glucose?
Question 16.6
Magic? The interconverison of DHAP and GAP greatly favors the formation of DHAP at equilibirum. Yet the conversion of DHAP by triose phosphate isomerase proceeds readily. Why?
Question 16.7
Between two extremes. What is the role of a thioester in the formation of ATP in glycolysis?
Question 16.8
Corporate sponsors. Some of the early research on glycolysis was supported by the brewing industry. Why would the brewing industry be interested in glycolysis?
Question 16.9
Recommended daily allowance. The recommended daily allowance for the vitamin niacin is 15 mg per day. How would glycolysis be affected by niacin deficiency?
Question 16.10
Who’s on first? Although both hexokinase and phosphofructokinase catalyze irreversible steps in glycolysis and the hexokinase-
490
Question 16.11
The tortoise and the hare. Why is the regulation of phosphofructokinase by energy charge not as important in the liver as it is in muscle?
Question 16.12
Like Minneapolis and St. Paul. Match each term with its description.
|
(a) Lactate _______ |
1. Generates oxaloacetate |
|
(b) Pyruvate carboxylase _______ |
2. Readily converted into DHAP |
|
(c) Acetyl CoA _______ |
3. Generates a high- |
|
(d) Phosphoenolpyruvate carboxykinase _______ |
4. Found predominantly in liver |
|
(e) Glycerol _______ |
5. Gluconeogenic counter- |
|
(f) Fructose 1,6- |
6. Readily converted into pyruvate |
|
(g) Glucose 6- |
7. Required for pyruvate carboxylase activity |
Question 16.13
Running in reverse. Why can’t the reactions of the glycolytic pathway simply be run in reverse to synthesize glucose?
Question 16.14
Road blocks. What reactions of glycolysis are not readily reversible under intracellular conditions?
Question 16.15
No pickling. Why is it in the muscle’s best interest to export lactic acid into the blood during intense exercise?
Question 16.16
Après vous. Why is it physiologically advantageous for the pancreas to use GLUT2, with a high KM, as the transporter that allows glucose entry into β cells?
Question 16.17
Bypass. In the liver, fructose can be converted into glyceraldehyde 3-
Question 16.18
Match ’em 1. The following sequence is a part of the sequence of reactions in gluconeogenesis.
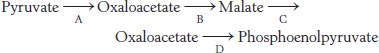
Match the capital letters representing the reaction in the gluconeogenic pathway with parts a, b, c, etc.
takes place in mitochondria
takes place in the cytoplasm
produces CO2
consumes CO2
requires NADH
produces NADH
requires ATP
requires GTP
requires thiamine
requires biotin
is regulated by acetyl CoA.
Question 16.19
Like Batman and Robin. Match parts a through j with parts 1 through 10.
|
(a) Glucose 6- |
1. Inhibits phosphofructokinase in the liver |
|
(b) [ATP], [AMP] _______ |
2. Glucokinase |
|
(c) Citrate _______ |
3. GLUT2 |
|
(d) Low pH _______ |
4. Inhibits hexokinase |
|
(e) Fructose 1, 6- |
5. Inhibits phosphofructo- |
|
(f) Fructose 2, 6 bisphosphate _______ |
6. Inhibits phosphofructokinase |
|
(g) Insulin _______ |
7. Stimulates pyruvate kinase |
|
(h) Has a high KM for glucose _______ |
8. Stimulates phosphofructokinase in the liver |
|
(i) Transporter specific to liver and pancreas _______ |
9. Causes the insertion of GLUT4 into cell membranes |
|
(j) [ATP] > [AMP] _______ |
10. Stimulates phosphofructokinase |
Question 16.20
Trouble ahead. Suppose that a microorganism that was an obligate anaerobe suffered a mutation that resulted in the loss of triose phosphate isomerase activity. How would this loss affect the ATP yield of fermentation? Could such an organism survive?
Question 16.21
Kitchen chemistry. Sucrose is commonly used to preserve fruits. Why is glucose not suitable for preserving foods?
Question 16.22
Tracing carbon atoms 1. Glucose labeled with 14C at C-
What is the distribution of 14C in the pyruvate that is formed? (Assume that the interconversion of glyceraldehyde 3-
phosphate and dihydroxyacetone phosphate is very rapid compared with the subsequent step.) If the specific activity of the glucose substrate is 10 mCi mmol−1 (millicuries per mole, a measure of radioactivity per mole), what is the specific activity of the pyruvate that is formed?
Question 16.23
Lactic acid fermentation.
Write a balanced equation for the conversion of glucose into lactate.
491
Calculate the standard free-
energy change of this reaction by using the data given in Table 16.1 and the fact that ΔG°′ is −25 kJ mol−1 (−6 kcal mol−1) for the following reaction: 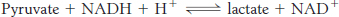
What is the free-
energy change (ΔG, not ΔG°′) of this reaction when the concentrations of reactants are: glucose, 5 mM; lactate, 0.05 mM; ATP, 2 mM; ADP, 0.2 mM; and Pi, 1 mM?
Question 16.24
High potential. What is the equilibrium ratio of phosphoenolpyruvate to pyruvate under standard conditions when [ATP]/[ADP] = 10?
Question 16.25
Hexose–
Question 16.26
Double labeling. 3-
Question 16.27
An informative analog. Xylose has the same structure as that of glucose except that it has a hydrogen atom at G-
Question 16.28
Distinctive sugars. The intravenous infusion of fructose into healthy volunteers leads to a two-
Why is glycolysis more rapid after the infusion of fructose?
Fructose has been used in place of glucose for intravenous feeding. Why is this use of fructose unwise?
Question 16.29
It is not hard to meet expenses. They are everywhere. What energetic barrier prevents glycolysis from simply running in reverse to synthesis glucose? What is the energetic cost to overcome this barrier?
Question 16.30
Match ’em 2. Indicate which of the conditions listed in the right-
|
(a) glycolysis _______ |
1. increase in ATP |
|
(b) gluconeogenesis _______ |
2. increase in AMP |
|
3. increase in fructose 2,6- |
|
|
4. increase in citrate |
|
|
5. increase in acetyl CoA |
|
|
6. increase in insulin |
|
|
7. increase in glucagon |
|
|
8. fasting |
|
|
9. fed |
Question 16.31
Waste not, want not. Why is the conversion of lactic acid from the blood into glucose in the liver in an organism’s best interest?
Question 16.32
Road blocks bypassed. How are the irreversible reactions of glycolysis bypassed in gluconeogenesis?
Question 16.33
Pointlessness averted. What are the regulatory means that prevent high levels of activity in glycolysis and gluconeogenesis simultaneously?
Question 16.34
Different needs. Liver is primarily a gluconeogenic tissue, whereas muscle is primarily glycolytic. Why does this division of labor make good physiological sense?
Question 16.35
Metabolic mutants. What would be the effect on an organism’s ability to use glucose as an energy source if a mutation inactivated glucose 6-
Question 16.36
Never let me go. Why does the lack of glucose 6-
Question 16.37
Counting high-
Question 16.38
Counting high-
Glucose 6-
phosphate Fructose 1,6-
bisphosphate Two molecules of oxaloacetate
Two molecules of dihydroxyacetone phosphate
Question 16.39
Lending a hand. How might enzymes that remove amino groups from alanine and aspartate contribute to gluconeogenesis?
Question 16.40
More metabolic mutants. Predict the effect of each of the following mutations on the pace of glycolysis in liver cells:
Loss of the allosteric site for ATP in phosphofructokinase
Loss of the binding site for citrate in phosphofructokinase
Loss of the phosphatase domain of the bifunctional enzyme that controls the level of fructose 2,6-
bisphosphate Loss of the binding site for fructose 1,6-
bisphosphate in pyruvate kinase
Question 16.41
Yet another metabolic mutant. What are the likely consequences of a genetic disorder rendering fructose 1,6-
Question 16.42
Biotin snatcher. Avidin, a 70-
492
Glucose → pyruvate
Pyruvate → glucose
Oxaloacetate → glucose
Malate → oxaloacetate
Pyruvate → oxaloacetate
Glyceraldehyde 3-
phosphate →fructose 1,6- bisphosphate
Question 16.43
Tracing carbon atoms 2. If cells synthesizing glucose from lactate are exposed to CO2 labeled with 14C, what will be the distribution of label in the newly synthesized glucose?
Question 16.44
Arsenate poisoning. Arsenate.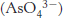 closely resembles Pi in structure and reactivity. In the reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-
closely resembles Pi in structure and reactivity. In the reaction catalyzed by glyceraldehyde 3-
Question 16.45
Reduce, reuse, recycle. In the conversion of glucose into two molecules of lactate, the NADH generated earlier in the pathway is oxidized to NAD+. Why is it not to the cell’s advantage to simply make more NAD+ so that the regeneration would not be necessary? After all, the cell would save much energy because it would no longer need to synthesize lactic acid dehydrogenase.
Question 16.46
Adenylate kinase again. Adenylate kinase, an enzyme considered in great detail in Chapter 9, is responsible for interconverting the adenylate nucleotide pool:

The equilibrium constant for this reaction is close to 1, inasmuch as the number of phosphoanhydride bonds is the same on each side of the equation. Using the equation for the equilibrium constant for this reaction, show why changes in [AMP] are a more effective indicator of the adenylate pool than [ATP].
Question 16.47
Working at cross-
Question 16.48
Powering pathways. Compare the stoichiometries of glycolysis and gluconeogenesis. Recall that the input of one ATP equivalent changes the equilibrium constant of a reaction by a factor of about 108 (Section 15.2). By what factor do the additional high-
Mechanism Problem
Question 16.49
Argument by analogy. Propose a mechanism for the conversion of glucose 6-
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 16.50
Not just for energy. People with galactosemia display central nervous system abnormalities even if galactose is eliminated from the diet. The precise reason for it is not known. Suggest a plausible explanation.
Question 16.51
Power to the rbc! Hexokinase in red blood cells has a KM of approximately 50 μM. Because life is hard enough as it is, let‘s assume that the hexokinase displays Michaelis–
Question 16.52
State function. Fructose 2,6-
Data Interpretation Problems
Question 16.53
Now, that’s unusual. Phosphofructokinase has recently been isolated from the hyperthermophilic archaeon Pyrococcus furiosus. It was subjected to standard biochemical analysis to determine basic catalytic parameters. The processes under study were of the form
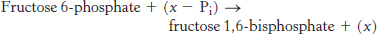
The assay measured the increase in fructose 1,6-
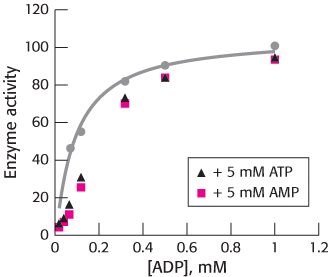
How does the P. furiosus phosphofructokinase differ from the phosphofructokinase considered in this chapter?
What effects do AMP and ATP have on the reaction with ADP?
Question 16.54
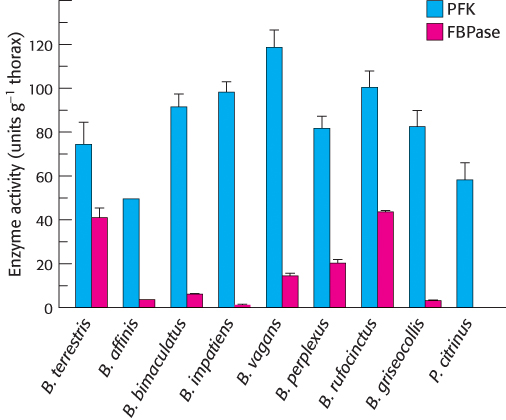
Cool bees. In principle, a futile cycle that includes phos-
493
What was the rationale for comparing the activities of these two enzymes?
The data below show the activites of both enzymes for a variety of bumblebee species (genera Bombus and Psithyrus). Do these results support the notion that bumblebees use futile cycles to generate heat? Explain.
In which species might futile cycling take place? Explain your reasoning.
Do these results prove that futile cycling does not participate in heat generation?
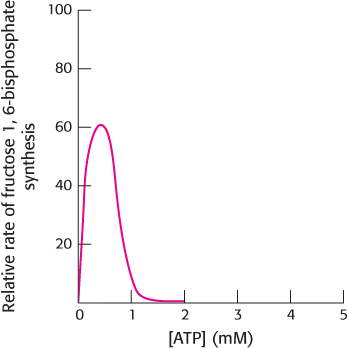
Question 16.55
Confused? The adjoining graph shows muscle phosphofructokinase activity as a function of ATP concentration in the presence of a constant concentration of fructose 6-
494