PROBLEMS
PROBLEMS
Question 20.1
A vital cycle. Why is the Calvin cycle crucial to the functioning of all life forms?
Question 20.2
Be nice to plants. Differentiate between autotrophs and heterotrophs.
Question 20.3
Cabalistic reactions? Why are the reactions of the Calvin cycle sometimes referred to as the dark reactions? Do they take place only at night or are they grim, secret reactions?
Question 20.4
Compare and contrast. Identify the similarities and differences between the Krebs cycle and the Calvin cycle.
Question 20.5
Labeling experiments. When Melvin Calvin performed his initial experiments on carbon fixation, he exposed algae to radioactive carbon dioxide. After 5 seconds, only a single organic compound contained radioactivity but, after 60 seconds, many compounds had incorporated radioactivity. (a) What compound in itially contained the radioactivity? (b) What compounds contained radioactivity after 60 seconds?
Question 20.6
Three-
Question 20.7
Not always to the swiftest. Suggest a reason why rubisco might be the most abundant enzyme in the world.
Question 20.8
A requirement. In an atmosphere devoid of CO2 but rich in O2, the oxygenase activity of rubisco disappears. Why?
Question 20.9
Reduce locally. Glyceraldehyde 3-
Question 20.10
Total eclipse. An illuminated suspension of the green alga Chlorella is actively carrying out photosynthesis. Suppose that the light is suddenly switched off. How would the levels of 3-
Question 20.11
CO2 deprivation. An illuminated suspension of Chlorella is actively carrying out photosynthesis in the presence of 1% CO2. The concentration of CO2 is abruptly reduced to 0.003%. What effect would this reduction have on the levels of 3-
Question 20.12
Salvage operation. Write a balanced equation for the transamination of glyoxylate to yield glycine.
Question 20.13
Dog days of August. Before the days of pampered lawns, most homeowners practiced horticultural Darwinism. A result was that the lush lawns of early summer would often convert into robust cultures of crabgrass in the dog days of August. Provide a possible biochemical explanation for this transition.
Question 20.14
Is it hot in here, or is it just me? Why is the C4 pathway valuable for tropical plants?
Question 20.15
No free lunch. Explain why maintaining a high concentration of CO2 in the bundle-
Question 20.16
Breathing pictures? What is photorespiration, what is its cause, and why is it believed to be wasteful?
Question 20.17
Global warming. C3 plants are most common in higher latitudes and become less common at latitudes near the equator. The reverse is true of C4 plants. How might global warming affect this distribution?
Question 20.18
Communication. What are the light-
615
Question 20.19
Match ‘em. Match each term with its description.
|
(a) Calvin cycle ____ (b) Rubisco ____ (c) Carbamate ____ (d) Starch ____ (e) Sucrose ____ (f) Amylose ____ (g) Amylopectin ____ (h) C3 plants ____ (i) C4 plants ____ (j) Stomata ____ |
1. Catalyzes CO2 fixation 2. Storage form of carbohydrates 3. α-1,4 linkages only 4. 3- 5. The dark reactions 6. Includes α-1,6 linkages 7. Required for rubisco activity 8. Carbon fixation results in oxaloacetate formation 9. Allow exchange of gases 10. Transport form of carbohydrates |
Question 20.20
Linked in. Describe how the pentose phosphate pathway and glycolysis are linked by transaldolase and transketolase.
Question 20.21
Biochemical taxonomy.
Identify 6-
phosphoglucono- δ-lactone. _____ Which reactions produce NADPH? _____
Identify ribulose 5-
phosphate. _____ What reaction generates CO2? _____
Identify 6-
phosphogluconate. _____ Which reaction is catalyzed by phosphopentose isomerase? _____
Identify ribose 5-
phosphate _____ Which reaction is catalyzed by lactonase? _____
Identify glucose 6-
phosphate. _____ Which reaction is catalyzed by 6-
phosphogluconate dehydrogenase? _____ Which reaction is catalyzed by glucose 6-
phosphate dehydrogenase? _____
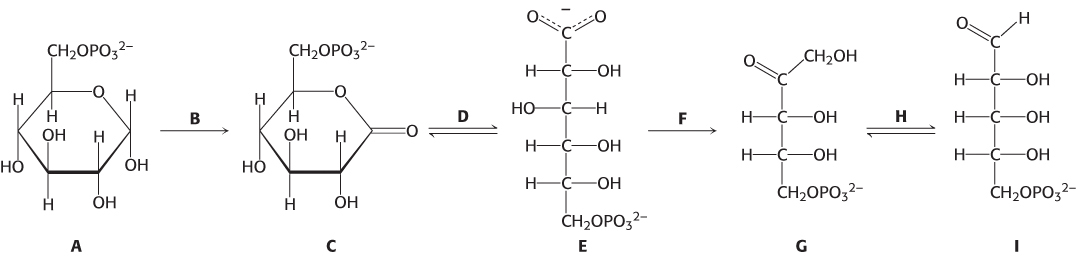
Question 20.22
Tracing glucose. Glucose labeled with 14C at C-
Question 20.23
Recurring decarboxylations. Which reaction in the citric acid cycle is most analogous to the oxidative decarboxylation of 6-
Question 20.24
Synthetic stoichiometries. What is the stoichiometry of the synthesis of (a) ribose 5-
Question 20.25
Offal or awful? Liver and other organ meats contain large quantities of nucleic acids. In the course of digestion, RNA is hydrolyzed to ribose, among other chemicals. Explain how ribose can be used as a fuel.
Question 20.26
A required ATP. The metabolism of glucose 6-
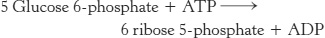
Which reaction requires the ATP?
Question 20.27
No respiration. Glucose is normally completely oxidized to CO2 in the mitochondria. In what circumstance can glucose be completely oxidized to CO2 in the cytoplasm?
Question 20.28
Watch your diet, doctor. The noted psychiatrist Hannibal Lecter once remarked to FBI Agent Clarice Starling that he enjoyed liver with some fava beans and a nice Chianti. Why might this diet be dangerous for some people?
Question 20.29
No redundancy. Why do deficiencies in glucose 6-
Question 20.30
Damage control. What is the role of glutathione in protection against damage by reactive peroxides? Why is the pentose phosphate pathway crucial to this protection?
Question 20.31
Reductive power. What ratio of NADPH to NADP+ is required to sustain [GSH] = 10 mM and [GSSG] = 1 mM? Use the redox potentials given in Table 18.1.
616
Mechanism Problems
Question 20.32
An alternative approach. The mechanisms of some aldolases do not include Schiff-
Question 20.33
A recurring intermediate. Phosphopentose isomerase interconverts the aldose ribose 5-
Chapter Integration Problems
Question 20.34
Catching carbons. Radioactive-
Question 20.35
You do what you can do. Red blood cells lack mitochondria. These cells process glucose to lactate, but they also generate CO2. What is the purpose of producing lactate? How can red blood cells generate CO2 if they lack mitochondria?
Question 20.36
Better to focus on one. Rubisco catalyzes both a carboxylation reaction and a wasteful oxygenase reaction. Below are the kinetic parameters for the two reactions.
|
KM CO2 (μM) |
KM O2 (μM) |
kcat CO2 (s−1) |
kcat O2 (s−1) |
|
10 |
500 |
3 |
2 |
Determine the values of
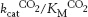 and
and 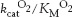 as s−1M−1.
as s−1M−1.In light of the kcat/KM values for the two reactions, why does the oxygenation reaction occur?
Question 20.37
Photosynthetic efficiency. Use the following information to estimate the efficiency of photosynthesis.
The ΔG°′ for the reduction of CO2 to the level of hexose is + 477 kJ mol−1 (+114 kcal mol−1).
A mole of 600-
Assume that the proton gradient generated in producing the required NADPH is sufficient to drive the synthesis of the required ATP.
Question 20.38
A violation of the First Law? The complete combustion of glucose to CO2 and H2O yields 30 ATP, as shown in Table 18.4. However, the synthesis of glucose requires only 18 ATP. How is it possible that glucose synthesis from CO2 and H2O requires only 18 ATP, but combustion to CO2 and H2O yields 30 ATP? Is it a violation of the First Law of Thermodynamics, or perhaps a miracle?
Data Interpretation Problem
Question 20.39
Deciding between 3 and 4. Graph A shows the photosynthetic activity of two species of plant, one a C4 plant and the other a C3 plant, as a function of leaf temperature.
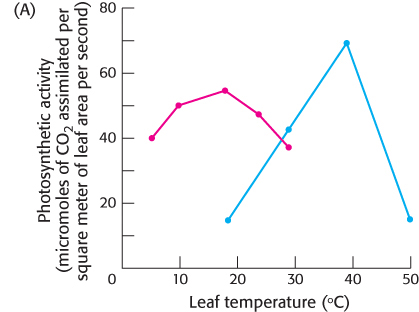
Which data were most likely generated by the C4 plant and which by the C3 plant? Explain.
Suggest some possible explanations for why the photosynthetic activity falls at higher temperatures.
Graph B illustrates how the photosynthetic activity of C3 and C4 plants varies with CO2 concentration when temperature (30°C) and light intensity (high) are constant.
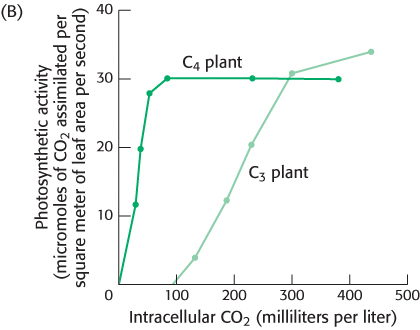
Why can C4 plants thrive at CO2 concentrations that do not support the growth of C3 plants?
Suggest a plausible explanation why C3 plants continue to increase photosynthetic activity at higher CO2 concentrations, whereas C4 plants reach a plateau.