12.1 Two-Way ANOVA
Skiing-related decisions (and many other behaviors) are routinely influenced by multiple variables, so we need a way to measure the interactive effects of multiple variables.
A two-way ANOVA is a hypothesis test that includes two nominal independent variables, regardless of their numbers of levels, and a scale dependent variable.
A two-way ANOVA (analysis of variance) allows us to compare levels from two independent variables plus the joint effects of those two variables. A two-way ANOVA is a hypothesis test that includes two nominal independent variables, regardless of their numbers of levels, and a scale dependent variable. We can also have ANOVAs with more than two independent variables. As the number of independent variables increases, the number increases in the name of the ANOVA—three-way, four-way, five-way, and so on. Table 12-1 shows a range of possibilities for naming ANOVAs.
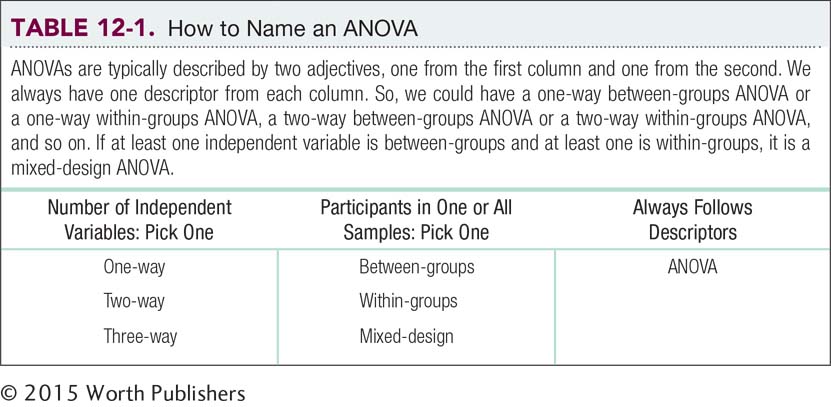
Regardless of the number of independent variables, we can use the research designs that we have already discussed. As with other hypothesis tests, a between-groups design is one in which every participant is in only one condition, and a within-groups design is one in which every participant is in all conditions. A mixed design is one in which one of the independent variables is between-groups and one is within-groups. In this chapter, we focus on the ANOVA that uses the second modifier from column 1 and the first modifier from column 2: the two-way between-groups ANOVA.
A factorial ANOVA is a statistical analysis used with one scale dependent variable and at least two nominal independent variables (also called factors); also called a multifactorial ANOVA.
Factor is a term used to describe an independent variable in a study with more than one independent variable.
Language Alert! There is a catch-all phrase for two-way, three-way, and higher-order ANOVAs; any ANOVA with at least two independent variables can be called a factorial ANOVA, a statistical analysis used with one scale dependent variable and at least two nominal independent variables (also called factors). This is also called a multifactorial ANOVA. Factor is another word used to describe an independent variable in a study with more than one independent variable.
In this section, we learn more about the situations in which we use a two-way ANOVA, as well as the language that is used in reference to this type of hypothesis test. Then we learn about the three outcomes we can examine with a two-way ANOVA.
Why We Use Two-Way ANOVA
Pharmaceutical researchers also understand the benefits of the two-way ANOVA. For example, numerous studies (e.g., Bailey & Dresser, 2004; Mitchell, 1999) have documented the potential for grapefruit juice to increase the blood levels of certain medications, sometimes to toxic levels, by boosting the absorption of one or more of the active ingredients. Even scarier, this potentially life-threatening increase cannot be predicted for a given individual. For that reason, many physicians suggest that patients who take a wide range of medications (from some blood pressure drugs to many antidepressants) avoid grapefruit juice entirely. One commonly used anticholesterol drug whose effect is moderately boosted, sometimes dangerously, by the consumption of grapefruit juice is Lipitor (e.g., Bellosta, Paoletti, & Corsini, 2004). Let’s use this particular interaction to understand how a two-way ANOVA gives us much more information with far less effort and expense than a one-way ANOVA.
Page 328
EXAMPLE 12.1
Let’s say that an investigator, Dr. Goldstein, wanted to know how to treat cholesterol but only knew how to analyze hypothesis tests that used one independent variable, the one-way between-groups ANOVA. She would conduct one study to compare the effect of Lipitor on cholesterol levels with the effect of another drug or a placebo. Then she would conduct a second study to compare the effect of grapefruit juice on cholesterol levels with that of another beverage or with no beverage, a study that might not even make much sense; after all, no one is predicting grapefruit juice on its own to be a treatment for high cholesterol. So how could she discover whether Lipitor works differently when combined with grapefruit juice?
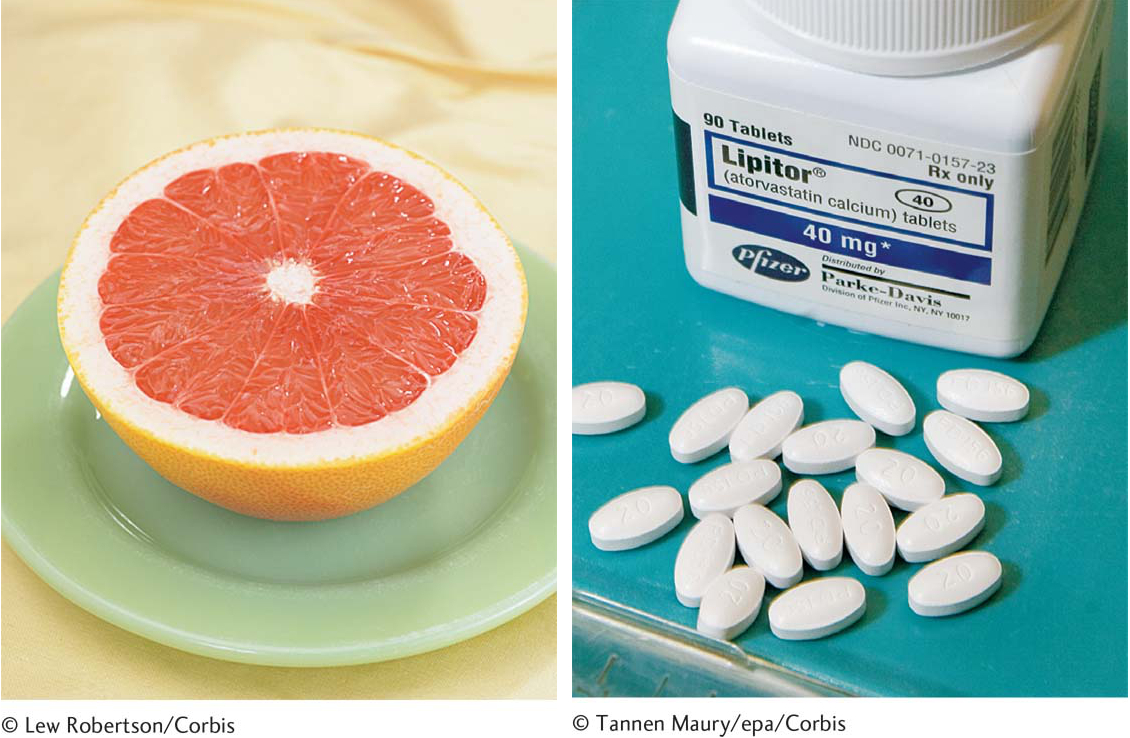
The Perils of Grapefruit Juice Drinking grapefruit juice (a level of one independent variable) can create an interaction with many common medications (levels of a second independent variable) to cause higher levels of active ingredients (the dependent variable) to be absorbed into the bloodstream. Two-way ANOVAs can reveal such potentially toxic interactions.
© Tannen Maury/epa/Corbis
A single study simultaneously examining medications like Lipitor and beverages like grapefruit juice is more efficient than two studies examining each independent variable separately. Two-way ANOVAs allow researchers to examine both hypotheses with the resources, time, and energy of a single study. But a two-way ANOVA yields even more information than two separate experiments.
Specifically, a two-way ANOVA allows researchers to explore exactly what Dr. Goldstein wanted to explore: interactions. Does the effect of some medications, but not others, depend on the particular levels of another independent variable, the beverages that accompany them? A two-way ANOVA can examine (1) the effect of Lipitor versus other medications, (2) the effect of grapefruit juice versus other beverages, and (3) the ways in which a drug and a juice might combine to create some entirely new, and often unexpected, effect.
The More Specific Vocabulary of Two-Way ANOVA
Every ANOVA, we learned, has two descriptors, one indicating the number of independent variables and one indicating the research design. Many researchers expand the first descriptor to provide even more information about the independent variables. Let’s consider these expanded descriptors in the context of Dr. Goldstein’s research. Were she to conduct just one study that examined both medication and beverage, she’d assign each participant to one level of medication (perhaps Lipitor, another cholesterol medication such as Zocor, or a placebo) and to one level of beverage (perhaps grapefruit juice or water). This research design is shown in Table 12-2.
Page 329
A cell is a box that depicts one unique combination of levels of the independent variables in a factorial design.
When we draw the design of a study, such as in Table 12-2, we call each box of the design a cell, a box that depicts one unique combination of levels of the independent variables in a factorial design. When cells contain numbers, they are usually means of the scores of all participants who were assigned to that combination of levels. Many social science researchers hope to have about 30 participants in each cell—that’s why experiments can quickly become very expensive. In Dr. Goldstein’s study, participants are assigned to one of the six cells. Each participant is randomly assigned to one of the three levels of the variable “medication” (Lipitor, Zocor, and placebo) listed in the columns of the table of cells.
Each participant is also assigned to one of the two levels of the variable “beverage” (grapefruit juice and water) listed in the rows of the table of cells. A participant might be assigned to Lipitor and grapefruit juice (upper-left cell), placebo and water (lower-right cell), or any of the other four combinations.
Language Alert! This leads us to the new ANOVA vocabulary. Instead of the descriptor two-way, many researchers refer to an ANOVA with this arrangement of cells as a 3 × 2 ANOVA (pronounced “three by two,” not “three times two”). As with the two-way descriptor, the ANOVA is described with a second modifier—usually between-groups or within-groups. Because participants would receive only one medication and only one beverage, the hypothesis test could be called either a two-way between-groups ANOVA or a 3 × 2 between-groups ANOVA. (An added benefit to the method of naming ANOVAs by the numbers of levels in each independent variable is the ease of calculating the total number of cells. Simply multiply the levels of the independent variables. In this case, the 3 × 2 ANOVA would have (3 × 2) = 6 cells.)
Two Main Effects and an Interaction
A main effect occurs in a factorial design when one of the independent variables has an influence on the dependent variable.
Two-way ANOVAs produce three F statistics: one for the first independent variable, one for the second independent variable, and one for the interaction between the two independent variables. The F statistics for each of the two independent variables describe main effects. A main effect occurs in a factorial design when one of the independent variables has an influence on the dependent variable. We evaluate whether there is a main effect by disregarding the influence of any other independent variables in the study—we temporarily pretend that the other variable doesn’t exist.
So, with two independent variables, Dr. Goldstein would have two possibilities for a main effect. For example, after testing her participants in a two-way ANOVA, she might find a main effect of “type of medication,” temporarily pretending that the variable “beverage” hasn’t even been included in the study. For example, Lipitor and Zocor might both work better than the placebo at lowering cholesterol. That’s the first F statistic. She also might find a main effect of “beverage,” temporarily pretending that the variable “medication” hasn’t even been included in the study. For example, drinking grapefruit juice may reduce cholesterol, at least as compared to drinking water. That’s the second F statistic.
Page 330
MASTERING THE CONCEPT
12-1: In a two-way ANOVA, we test three different effects—two main effects (one for each independent variable), and one interaction (the joint effect of the two independent variables).
The third F statistic in a two-way ANOVA has the potential to be the most interesting because it is complicated by multiple, interacting variables. For example, Dr. Goldstein might find that both Lipitor and Zocor (but not the placebo) have more extreme effects on cholesterol when taken in combination with grapefruit juice versus water. In other words, the presence of the grapefruit juice changes the effects of Lipitor and Zocor, but not that of the placebo.
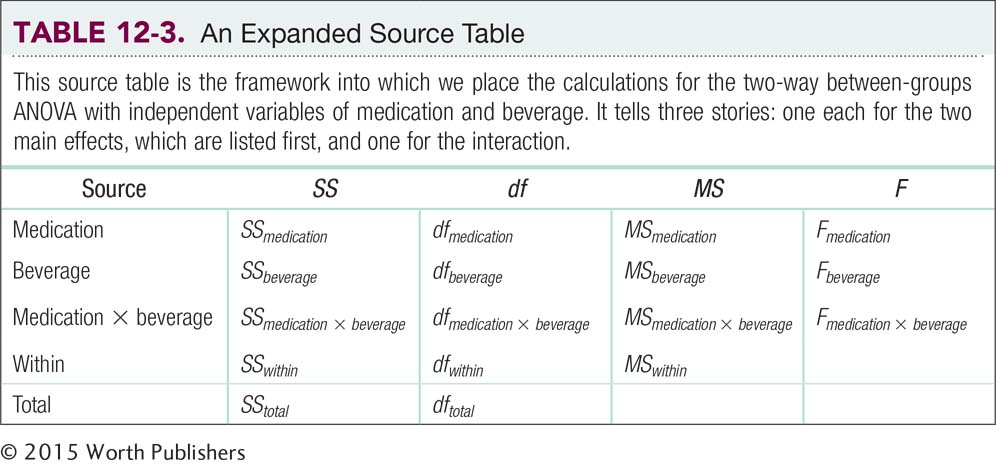
Each of the three F statistics has its own between-groups sum of squares (SS), degrees of freedom (df ), mean square (MS ), and critical value, but they all share a within-groups mean square (MSwithin). The source table is shown in Table 12-3. The symbols in the body of the table are replaced by the specific values of these statistics in an actual source table.
CHECK YOUR LEARNING
| Reviewing the Concepts |
|
Factorial ANOVAs are used with multiple independent variables because they allow us to examine several hypotheses in a single study and explore interactions. Factorial ANOVAs are often referred to by the levels of their independent variables (e.g., 2 × 2) rather than the number of independent variables (e.g., two-way). Sometimes the independent variables are called factors. A two-way ANOVA can have two main effects (one for each independent variable) and one interaction (the combined influence of both variables). Each effect and interaction has its own set of statistics, including its own F statistic, which are displayed in an expanded source table.
|
| Clarifying the Concepts |
12-1 |
What is a factorial ANOVA? |
|
12-2 |
What is an interaction? |
| Calculating the Statistics |
12-3 |
What is an interaction? Determine how many factors are in each of the following designs:
The effect of three diet programs and two exercise programs on weight loss. The effect of three diet programs, two exercise programs, and three different personal metabolism types on weight loss. The effect of gift certificate value ($15, $25, $50, and $100) on the amount people spend over that value. The effect of gift certificate value ($15, $25, $50, and $100) and store quality (low end versus high end) on consumer overspending.
|
| Applying the Concepts |
12-4 |
Adam Alter, a graduate student at Princeton University, and his advisor, Daniel Oppenheimer, studied whether names of stocks affected selling prices (Alter & Oppenheimer, 2006). They found that stocks with pronounceable ticker-code names, like “BAL,” tended to sell at higher prices than did stocks with unpronounceable names, like “BDL.” They examined this effect 1 day, 1 week, 6 months, and 1 year after the stock was offered for sale. The effect was strongest 1 day after the stocks were initially offered.
What are the “participants” in this study? What are the independent variables and what are their levels? What is the dependent variable? Using the descriptors from Chapter 11, what would you call the hypothesis test that would be used? Using the new descriptors from this chapter, what would you call the hypothesis test that would be used? How many cells are there? Explain how you calculated this answer.
|
Solutions to these Check Your Learning questions can be found in Appendix D.
Page 331