EXAMPLE 7Analyzing a Limit
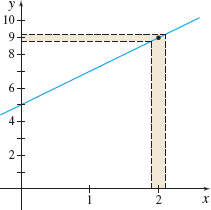
In Example 1, we claimed that lim.
- (a) How close must x be to 2, so that f(x) =2x+5 is within 0.1 of 9?
- (b) How close must x be to 2, so that f(x) =2x+5 is within 0.05 of 9?
On the number line, the distance between two points with coordinates {a} and b is \vert{a-b}\vert.
Solution (a) The function f(x)=2x+5 is within 0.1 of 9, if the distance between f(x) and 9 is less than 0.1 unit. That is, if \vert f(x)-9\vert\leq 0.1. \begin{eqnarray*} \vert (2x+5) -9\vert &\leq &0.1 \\ \vert 2x-4\vert &\leq &0.1 \\ \vert 2( x-2) \vert &\leq &0.1 \\ \vert x-2\vert &\leq &\dfrac{0.1}{2}=0.05 \\ -0.05 &\leq &x-2\leq 0.05 \\ 1.95 &\leq &x\leq 2.05 \end{eqnarray*}
Inequalities involving absolute values are discussed in Appendix A.1, p. A-7.
So, if 1.95\leq x\leq 2.05, then f(x) will be within 0.1 of 9.
(b)The function f(x)=2x+5 is within 0.05 of 9 if \vert f(x) -9\vert \leq 0.05. That is, \begin{eqnarray*} \vert ( 2x+5) -9\vert &\leq &0.05 \\ \vert 2x-4\vert &\leq &0.05 \\ \vert x-2\vert &\leq &\dfrac{0.05}{2}=0.025 \end{eqnarray*}
So, if 1.975\leq x\leq 2.025, then f(x) will be within 0.05 of 9.