The Geographer’s Toolkit
GT
LIVING PHYSICAL GEOGRAPHY
Where do tornadoes get their energy?
How do my car and phone know where I am?
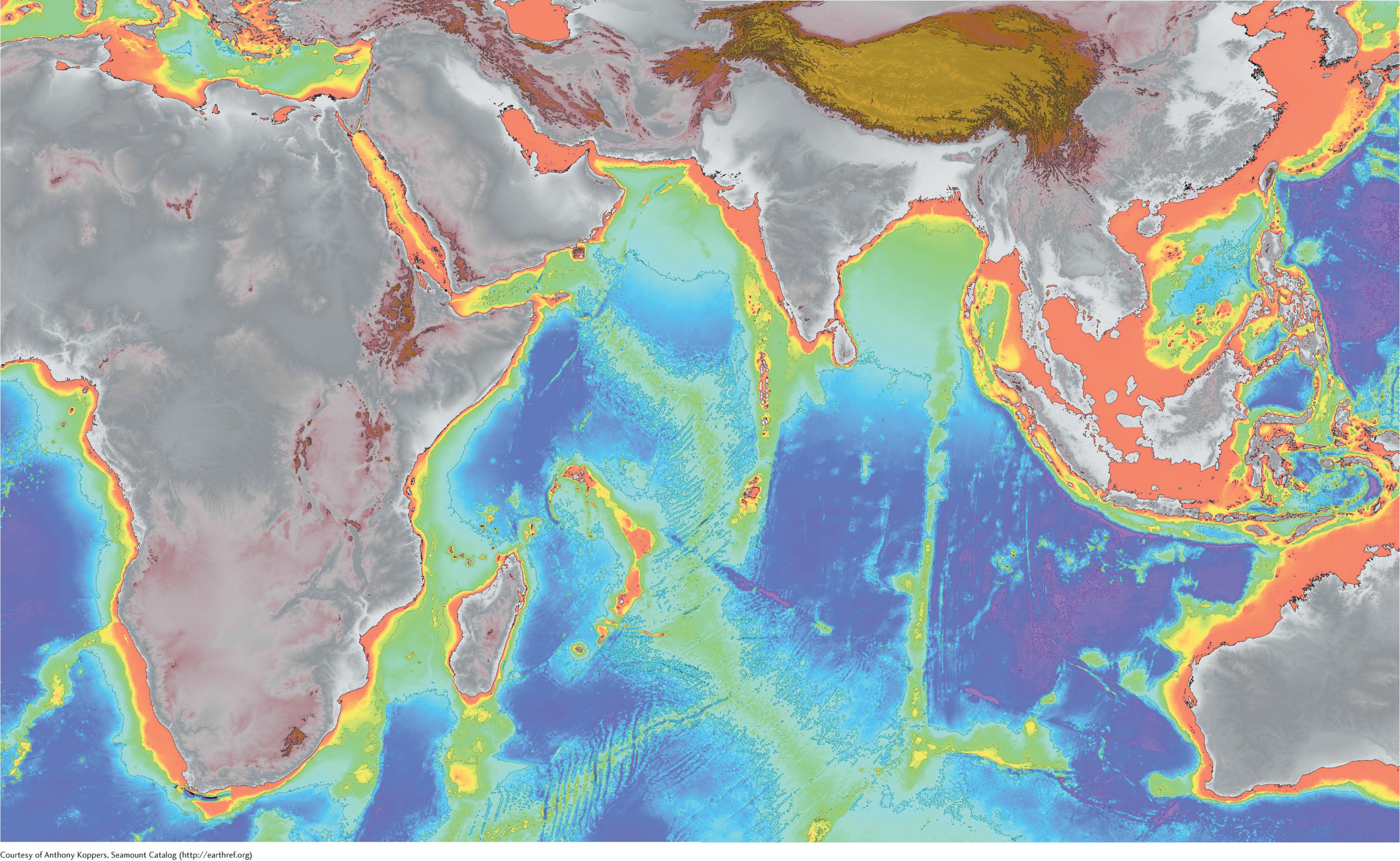
How do we know mountains are hidden deep in the ocean?
Who built the massive statues on Easter Island and how?
THE BIG PICTURE
Physical geography studies how Earth’s natural systems function, how they change naturally through space and time, and how people change them.
LEARNING GOALS
After reading this chapter, you will be able to:
GT.1
Define physical geography and explain different scales of geographic inquiry.
GT.2
Describe Earth’s major physical systems and their characteristics.
GT.3
Use the geographic grid coordinate system to identify locations on Earth’s surface and distinguish among different types of maps often employed in physical geography.
GT.4
Discuss how technologies such as satellite sensors and radar are used to study and portray Earth systems and processes.
GT.5
Apply the scientific method to Easter Island to study its history of human settlement.