PROBLEMS
WORKING WITH THE FIGURES
Question 1
Figure 10-1 shows that specific DNA fragments can be synthesized in vitro prior to cloning. What are two ways to synthesize DNA inserts for recombinant DNA in vitro?
Question 2
In Figure 10-4, why is cDNA made only from mRNA and not also from tRNAs and ribosomal RNAs?
Question 3
Redraw Figure 10-6 with the goal of adding one EcoRI end and one XhoI end. Below is the Xhol recognition sequence.
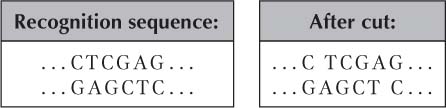
Question 4
Redraw Figure 10-7 so that the cDNA can insert into an XhoI site of a vector rather than into an EcoRI site as shown
Question 15
In Figure 10-10, determine approximately how many BAC clones are needed to provide 1 × coverage of
the yeast genome (12 Mbp).
the E. coli genome (4.1 Mbp).
the fruit-
fly genome (130 Mbp).
Question 6
In Figure 10-14, why does DNA migrate to the anode (+ pole)?
Question 7
In Figure 10-17a, why are DNA fragments of different length and all ending in an A residue synthesized?
Question 8
As you will see in Chapter 15, most of the genomes of higher eukaryotes (plants and animals) are filled with DNA sequences that are present in hundreds, even thousands, of copies throughout the chromosomes. In the chromosome-
Question 9
Redraw Figure 10-23 to include the positions of the single and double crossovers.
Question 10
In Figure 10-25, why do only plant cells that have T-
Question 11
In Figure 10-27, what is the difference between extrachromosomal DNA and integrated arrays of DNA? Are the latter ectopic? What is distinctive about the syncytial region that makes it a good place to inject DNA?
BASIC PROBLEMS
Question 12
From this chapter, make a list of all the examples of (a) the hybridization of single-
Question 13
Compare and contrast the use of the word recombinant as used in the phrases (a) “recombinant DNA” and (b) “re-
Question 14
Why is ligase needed to make recombinant DNA? What would be the immediate consequence in the cloning process if someone forgot to add it?
Question 15
In the PCR process, if we assume that each cycle takes 5 minutes, how manyfold amplification would be accomplished in 1 hour?
Question 16
The position of the gene for the protein actin in the hap-
Question 17
You obtain the DNA sequence of a mutant of a 2-
Question 18
In a T-
Question 19
How would you produce a mouse that is homozygous for a rat growth-
Question 20
Why was cDNA and not genomic DNA used in the commercial cloning of the human insulin gene?
Question 21
After Drosophila DNA has been treated with a restriction enzyme, the fragments are inserted into plasmids and selected as clones in E. coli. With the use of this “shotgun” technique, every DNA sequence of Drosophila in a library can be recovered.
How would you identify a clone that contains DNA encoding the protein actin, whose amino acid sequence is known?
How would you identify a clone encoding a specific tRNA?
Question 22
In any particular transformed eukaryotic cell (say, of Saccharomyces cerevisiae), how could you tell if the transforming DNA (carried on a circular bacterial vector)
replaced the resident gene of the recipient by double crossing over or single crossing over?
was inserted ectopically?
Question 23
In an electrophoretic gel across which is applied a powerful electrical alternating pulsed field, the DNA of the haploid fungus Neurospora crassa (n = 7) moves slowly but eventually forms seven bands, which represent DNA fractions that are of different sizes and hence have moved at different speeds. These bands are presumed to be the seven chromosomes. How would you show which band corresponds to which chromosome?
Question 24
The protein encoded by the cystic fibrosis gene is 1480 amino acids long, yet the gene spans 250 kb. How is this difference possible?
Question 25
In yeast, you have sequenced a piece of wild-
Question 26
Why is it necessary to use a special DNA polymerase (Taq polymerase) in PCR?
Question 27
For each of the following experimental goals, is PCR or gene cloning preferable and why?
Isolate the same gene from 20 individuals.
Isolate 100 genes from the same individual.
Isolate a mouse gene when you have a rat gene fragment.
Question 28
In Northern blotting, electrophoresis is used to resolve which biological molecules? What type of probe is used to identify the target molecule(s)?
Question 29
One feature that virtually all plasmid vectors have in common is the polylinker (also called a multiple cloning site). Explain what a polylinker is and why it is such an important feature.
Question 30
A second feature that virtually all plasmid vectors have in common is the selectable marker. Explain what this is and why it is such an important feature.
CHALLENGING PROBLEMS
Question 31
Prototrophy is often the phenotype selected to detect transformants. Prototrophic cells are used for donor DNA extraction; then this DNA is cloned and the clones are added to an auxotrophic recipient culture. Successful transformants are identified by plating the recipient culture on minimal medium and looking for colonies. What experimental design would you use to make sure that a colony that you hope is a transformant is not, in fact,
a prototrophic cell that has entered the recipient culture as a contaminant?
a revertant (mutation back to prototrophy by a second mutation in the originally mutated gene) of the auxotrophic mutation?
Question 32
A cloned fragment of DNA was sequenced by using the dideoxy chain-
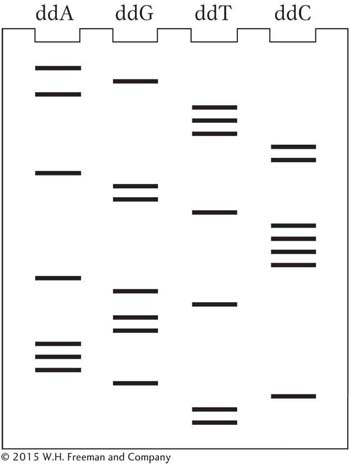
Deduce the nucleotide sequence of the DNA nucleotide chain synthesized from the primer. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends.
Deduce the nucleotide sequence of the DNA nucleotide chain used as the template strand. Label the 5′ and 3′ ends.
Write out the nucleotide sequence of the DNA double helix (label the 5′ and 3′ ends).
Question 33
The cDNA clone for the human gene encoding tyrosinase was radioactively labeled and used in a Southern analysis of EcoRI-
Question 34
Transgenic tobacco plants were obtained in which the vector Ti plasmid was designed to insert the gene of interest plus an adjacent kanamycin-
Question 35
A cystic-
Question 36
Bacterial glucuronidase converts a colorless substance called X-
Question 37
The plant Arabidopsis thaliana was transformed by using the Ti plasmid into which a kanamycin-

Draw the relevant plant chromosomes in both plants.
Explain the two different ratios.