Chapter 10Printed Page AN-47
1. True
2. False
3. True
4. True
5. Sphere
6. (0, 0, 0)
7. (1, 1, 1)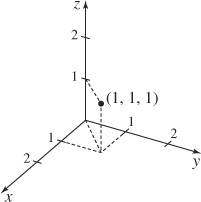
9. (0, 2, 5)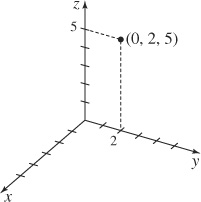
11. (−3, 1, 0)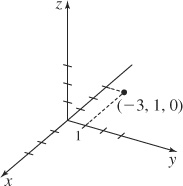
13. (2, 0, 0), (0, 1, 0), (0, 0, 3), (2, 1, 0), (2, 0, 3), (0, 1, 3)
15. (1, 4, 3), (3, 4, 3), (3, 2, 3), (1, 2, 5), (1, 4, 5), (3, 2, 5)
17. (−1, 0, 5), (4, 2, 2), (−1, 2, 2), (4, 0, 5), (4, 0, 2), (−1, 2, 5)
19. A plane parallel to the xz plane passing through the point (0,−2, 0)
21. A plane in space, also known as the yz-plane
23. A line parallel to the z-axis through the point (1, 0, 0)
25. The region of space where x > −2 and the y and z values are any real numbers
27. All points whose distance from the origin is at most 1.
29. 5
31. 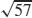
33. 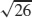
35. (x − 3)2 + (y − 1)2 + (z − 1)2 = 1
37. (x +1)2 + (y −1)2 + (z−2)2 = 9
39. Radius 2; center (−1, 1, 0)
41. Radius 3; center (−2, 2,−1)
43. Radius  ; center
; center 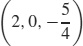
45. x2 + (y − 3)2 + (z − 6)2 = 17
47. (x + 3)2 + (y − 2)2 + (z − 1)2 = 62
49. (x − 2)2 + (y − 1)2 + (z + 2)2 = 4
51. (a) (0, 0, 0), (0.287, 0, 0), (0.287, 0.287, 0), (0, 0.287, 0), (0, 0, 0.287), (0.287, 0, 0.287), (0, 0.287, 0.287), (0.287, 0.287, 0.287), (0.1435, 0.1435, 0.1435)
(b) (0.287, 0.287, 0.287)
(c) (0.1435, 0.1435, 0.1435)
(d) ≈0.249
53. (a) (x − 4)2 + y2 + (z + 2)2 = 25
(b) Answers will vary.
55. 1
57. (x − 1)2 + (y + 2)2 + (z + 1)2 = 9
1. True
2. Magnitude
3. Scalar multiple
4. (a); (d)
5. Scalars: (a), (b), (d), (e), (f), (g). Vectors: (c), (h)
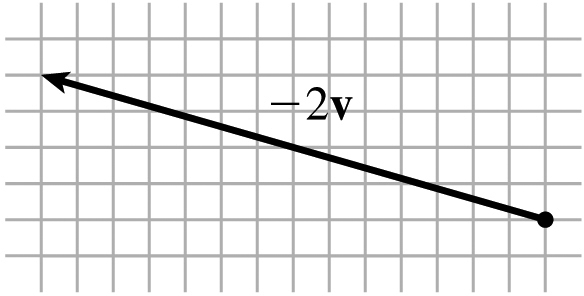
7. 
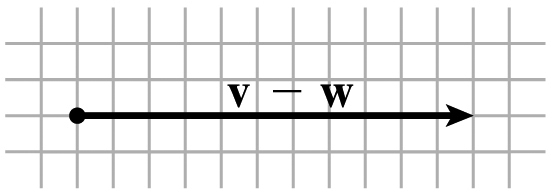
9. 
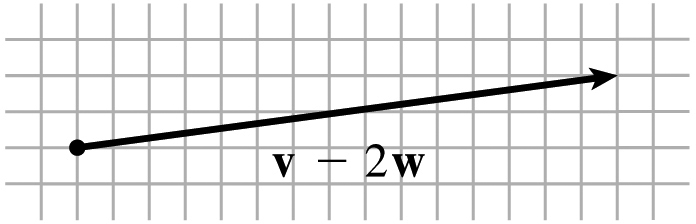
11. 
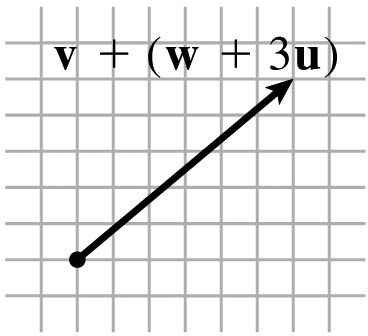
13. 
15. x = A
17. C = −D − E − F
19. E = G + H − D
21. 0
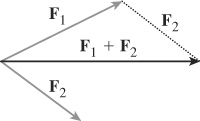
23. 
25. (a) 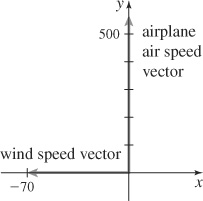
(b) 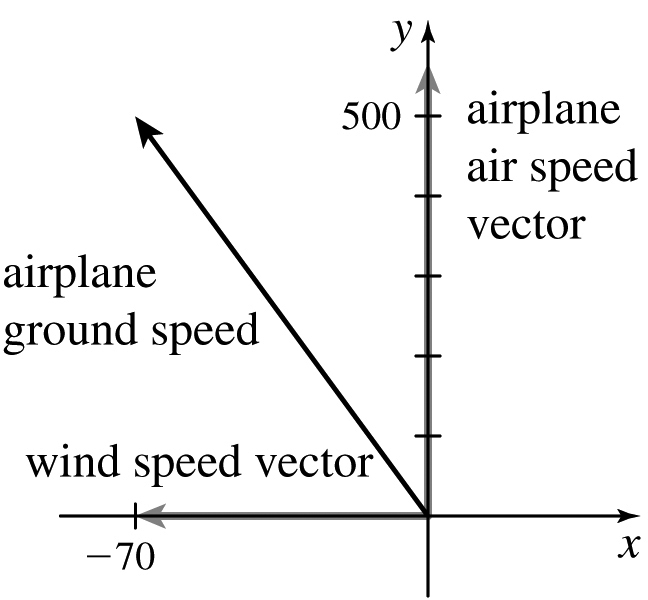
(c) Answers will vary.
27. u = 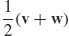
1. 〈1, 0, 0〉; 〈0, 1, 0〉; 〈0, 0, 1〉
2. Unit
3. Components
4. True
5. False
6. True
7. 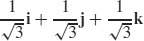
8. False
9. (a) 〈4,−5〉
(b) 4i−5j
11. (a) 〈−1, 1〉
(b) −i+j
13. (a) 〈−3,−2, 1〉
(b) −3i−2j+k
15. (a) 〈3, 0,−1〉
(b) 3i−k
17. 〈9,−4〉
19. 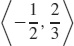
21. 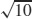
23. 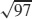
25. 〈15, 2, 20〉
27. 〈−19,−2,−28〉
29. 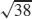
31. 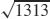
33. 5
35. 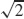
37. 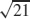
39. 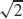
41. 1
43. 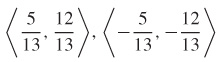
45. 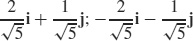
47. 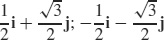
49. 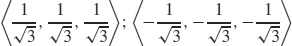
51. 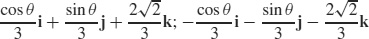
53. 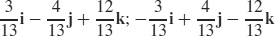
55. 3i − 8j
57. 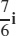
59. 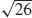
61. −3i + j − 5k
63. 17i − 3j + 13k
65. 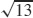
67. 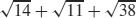
69. 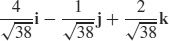
71. Parallel; same
73. Not parallel
75. Parallel; opposite
77. 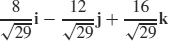
79. a = ±1
81. x = −5, 1
83. 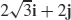
85. 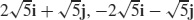
87. −i + j
89. 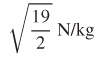
91. (a) (0, −2), (2,−4), (6,−1), (4, 1)
(b) 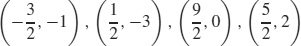
93. 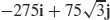
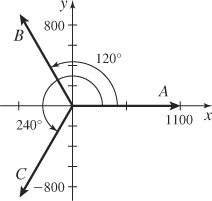
95. F = 3i − 4j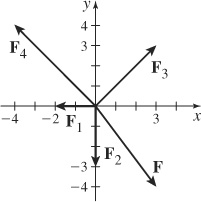
97. Left: ≈1000 lb; right: ≈845.237 lb.
99. (a) 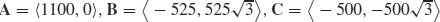
(b) 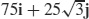
101. 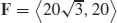
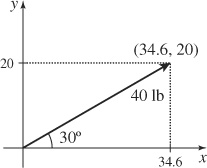
103. (a) (0, 0, 0), (0.408, 0, 0), (0, 0.408, 0), (0, 0, 0.408), (0.408, 0.408, 0), (0.408, 0, 0.408), (0, 0.408, 0.408), (0.408, 0.408, 0.408), (0.204, 0, 0.204), (0, 0.204, 0.204), (0.204, 0.204, 0), (0.204, 0.408, 0.204), (0.204, 0.204, 0.408), (0.408, 0.204, 0.204)
(b) (i) 0.408i + 0.408j + 0.408k (ii) 0.204i + 0.408j + 0.204k (iii) 0.204i + 0.204j + 0.408k
(c) ≈0.707; ≈0.500; ≈0.500
105.  from northwest
from northwest
107. See Student Solutions Manual.
109. See Student Solutions Manual.
111. 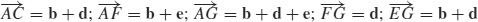
113. See Student Solutions Manual.
1. False
2. False
3. 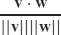
4. True
5. False
6. True
7. (a) 6
(b) ≈0.388 radians
9. (a) −1
(b) 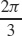
11. (a) −8
(b) ≈2.967 radians
13. (a) 0
(b) 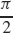
15. a = 1
17. a = −2
19. (a) 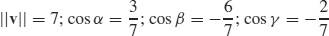
(b) 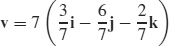
21. (a) 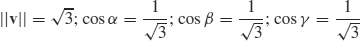
(b) 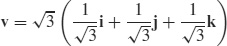
23. (a) 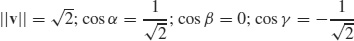
(b) 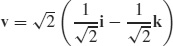
25. (a) 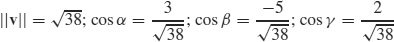
(b) 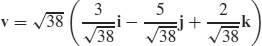
27. (a) projwv = 2i − 2j + 2k
(b) v1 = 2i − 2j + 2k; v2 = −j − k
29. (a) 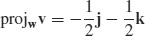
(b) 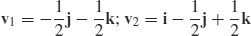
31. (a) 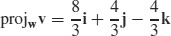
(b) 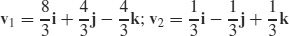
33. a = 0, a = 4
35. Speed ≈ 459.536 km/h, direction ≈ 84.703◦.
37. The boat should be steered at an angle of about 70.529° to the shore.
39. 737.618 lb, 5248.420 lb
41. 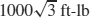
43. 2 J
45. (a) 7361.216 J; 6010.408 J
(b) Answers will vary.
47. See Student Solutions Manual.
49. See Student Solutions Manual.
51. 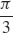
53. 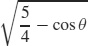
55. 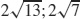
57. See Student Solutions Manual.
59. See Student Solutions Manual.
61. See Student Solutions Manual.
63. 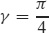
65. v = 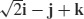
67. v = 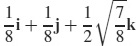
69. v = 0
71. See Student Solutions Manual.
73. See Student Solutions Manual.
75. See Student Solutions Manual.
77. 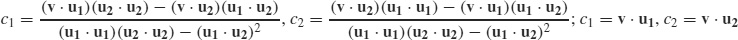
79. See Student Solutions Manual.
81. See Student Solutions Manual.
83. See Student Solutions Manual.
85. See Student Solutions Manual.
87. See Student Solutions Manual.
89. 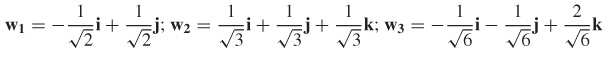
91. 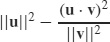
93. x + y ≥ 0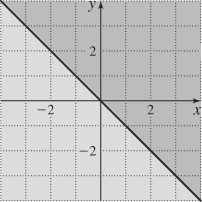
1. True
2. False
3. (b)
4. False
5. (d)
6. True
7. (c)
8. False
9. 2
11. 5
13. (a) −3j − 3k
(b) See Student Solutions Manual.
15. (a) −i + j − k
(b) See Student Solutions Manual.
17. (a) −i + j + 5k
(b) See Student Solutions Manual.
19. (a) −6i + 21j − 58k
(b) See Student Solutions Manual.
21. (a) −8i + 12j + 5k
(b) See Student Solutions Manual.
23. 0
25. i − 13j − 4k
27. 3i − 39j − 12k
29. i − 13j − 4k; Answers will vary.
31. 2i − 2j; Answers will vary.
33. 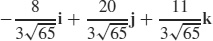 , the opposite of the given vector is also correct
, the opposite of the given vector is also correct
35. 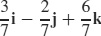 , the opposite of the given vector is also correct
, the opposite of the given vector is also correct
37. 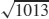
39. 58
41. 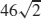
43. 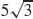
45. 58
47. 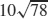 m/s
m/s
49. See Student Solutions Manual.
51. (a) Answers will vary.
(b)
τ1=1252kNm; τ2=125√24kNm; τ3=0Nm
(c) Answers will vary.
53. 0.0138125i − 0.015625j − 0.0036125k N
55. See Student Solutions Manual.
57. See Student Solutions Manual.
59. Answers will vary.
61. −21
63. See Student Solutions Manual.
65. See Student Solutions Manual.
67. 249
69. See Student Solutions Manual.
71. See Student Solutions Manual.
73. See Student Solutions Manual.
75. See Student Solutions Manual.
77. See Student Solutions Manual.
79. (a) ||v|| = 8.49 × 105 m/s; The velocity v is parallel to -k.
(b) Answers will vary.
81. (a) 0 N, south to north
(b) 0.05 N, east to west
(c) 30°
1. False
2. False
3. True
4. False
5. False
6. Answers will vary.
7. Answers will vary.
8. Skew
9. (a) r(t) = (1 + 2t)i + (2 − t)j + (3 + t)k
(b) x = 1 + 2t, y = 2 − t, z = 3 + t
(c) 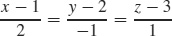
11. (a) r(t) = (1 + 3t)i + (−1 + 3t)j + (3 − 2t)k
(b) x = 1 + 3t; y = −1 + 3t; z = 3 − 2t
(c) 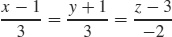
13. x = −1 + 5t, y = 5 + 4t, z = 6 − 3t
15. Answers will vary.
17. y = 2, 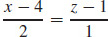
19. 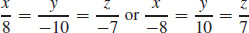
21. x = 1, 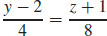
23. (a, b) Parallel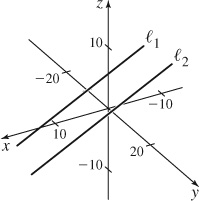
25. (a, b) Intersect when 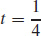 at the point (17/4, 11/4, 3/2)
at the point (17/4, 11/4, 3/2)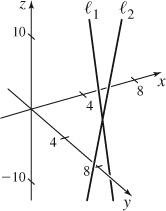
27. (a, b) Parallel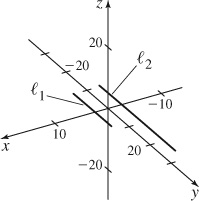
29. (a, b) Skew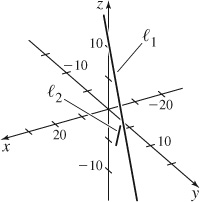
31. 2x − y + z = 5
33. x + 2y − z = 12
35. 2x + 5y − 2z = 21
37. z = 4
39. y = −2
41. (a) x + y + 3z = 0
(b) 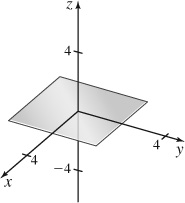
43. (a) 3x +7y −6z = 11
(b) 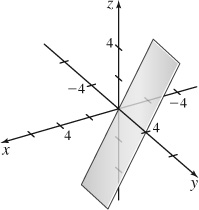
45. (a) 2x +6y +29z = 2
(b) 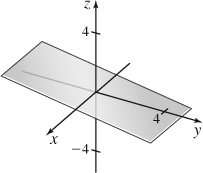
47. 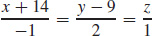
49. 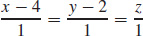
51. 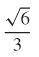
53. 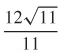
55. 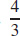
57. 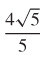
59. (3, 1, 2)
61. (4,−2, 3)
63. 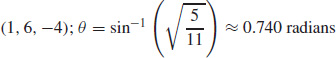
65. 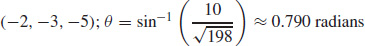
67.
(a) x (t) = 1 + 2t, y (t) = 2 − t, z (t) = −1 + t
(b) 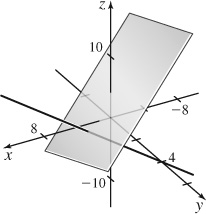
69. ℓ1 and ℓ2 are perpendicular.
71. 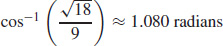
73. 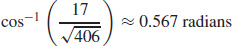
75. 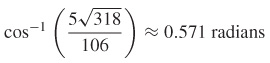
77. (a) Each path is a straight line.
(b) 0.889
(c) The paths do intersect.
(d) No. Answers will vary.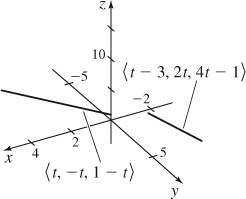
79. x = 1 + 3t, y = 3t, z = −1; Answers will vary.
81. 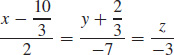
83. (4, 0, −4)
85. x + y − 2z = 1
87. 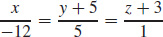
89. (a) See Student Solutions Manual.
(b) See Student Solutions Manual.
(c) Answers will vary.
91. See Student Solutions Manual.
93. 
1. (c)
2. (1, 0, 0),(−1, 0, 0),(0, 0,−4)
3. True
4. (b)
5. Hyperbolic cylinder
6. Saddle point
7. (a) Elliptic paraboloid
(b) Intercept: (0, 0, 0); traces: (0, 0, 0) in the xy-plane, z = x2 in the xz-plane, z = y2 in the yz-plane
(c) 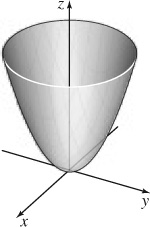
9. (a) Ellipsoid
(b) Intercepts: (1, 0, 0),(−1, 0, 0),(0, 2, 0),(0,−2, 0),(0, 0, 1) and (0, 0,−1); traces 4x2 + y2 + 4 in the xy-plane, x2 + z2 = 1 in the xz-plane, y2 + 4z2 = 4 in the yz-plane
(c) 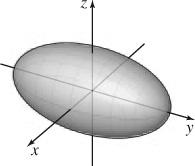
11. (a) Elliptic cone
(b) Intercept: (0, 0, 0); traces (0, 0, 0) in the xy-plane, z = ±x in the xz-plane, 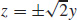 in the yz-plane.
in the yz-plane.
(c) 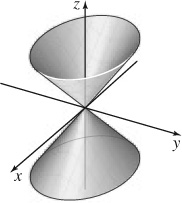
13. (a) Parabolic cylinder
(b) Traces x = 4z2 in the xz-plane, x = 0 in the xy-plane, z = 0 in the yz-plane
(c) 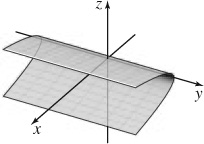
15. (a) Hyperboloid of two sheets
(b) Intercepts: (0, 0, 2) and (0, 0,−2); traces: ellipses defined for |z| > 2 parallel to the xy-plane, 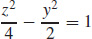 in the yz-plane,
in the yz-plane,  in the xz-plane
in the xz-plane
(c) 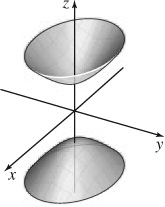
17. (a) Parabolic cylinder
(b) Intercepts: z = 0; trace 2x = y2 in the xy-plane
(c) 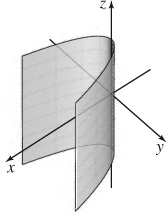
19. C
21. B
23. E
25. L
27. K
29. J
31. Answers will vary.
33. (a) 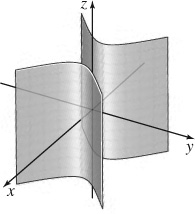
(b) 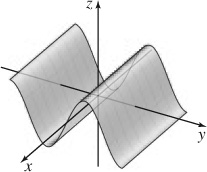
(c) 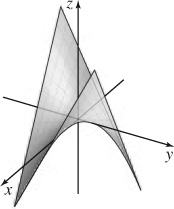
1. (1, 0, 4), (2, 3, 2), (2, 0, 2), (2, 0, 4), (1, 3, 4), (1, 3, 2)
3.
(a) v = 〈2, 1, 5〉
(b) v = 2i + j + 5k
5. 7
7. Center (2,−4, 0); radius 5
9. 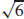
11. 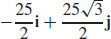
13. (a)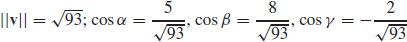
(b)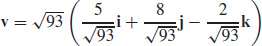
15. 9 J
17. 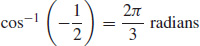
19. 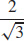
21. x = 1 + 3t, y = 3t, z = −1
23. a = 12
25. 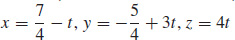
27. (a) 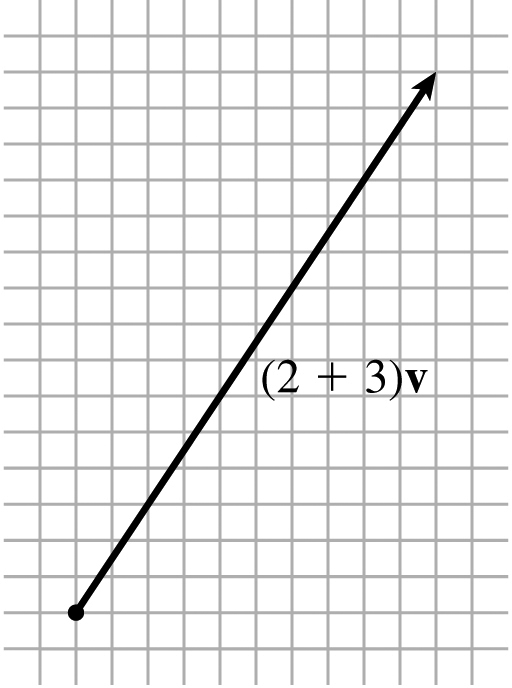
(b) 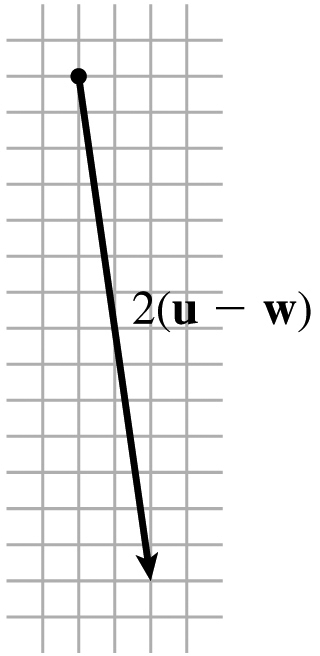
(c) 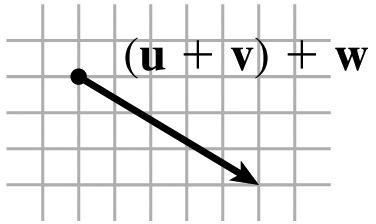
(d) 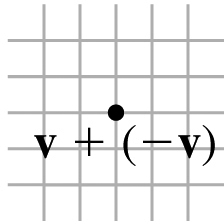
(e) 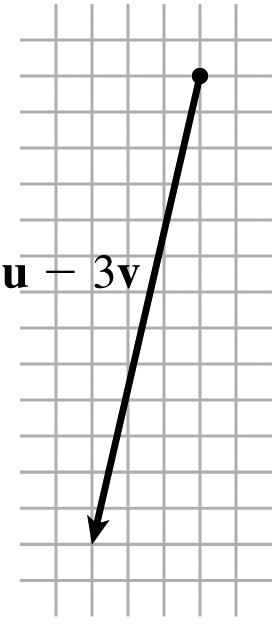
29. 2x + 3y + z = 5
31. 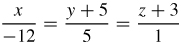
33. (a) Hyperbolic cylinder
(b) Intercepts: (2, 0, 0) and (−2, 0, 0); trace in the xy-plane is 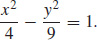 ; the traces in the xz-plane are x = −2 and x = 2.
; the traces in the xz-plane are x = −2 and x = 2.
(c) 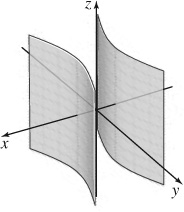
35. (a) Hyperbolic paraboloid.
(b) Intercept: (0, 0, 0); traces: xy-plane, the pair of lines y3=±x2,
which intersect at the origin. The trace in the xz-plane is the parabola z=14x2, and the trace in the yz-plane is the parabola z=−19y2.
(c) 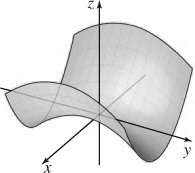
37. (a) Ellipsoid
(b) Intercepts: (2, 0, 0), (−2, 0, 0), (0, 3, 0), (0,−3, 0), (0, 0, 1), (0, 0,−1); traces: xy-plane, 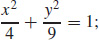 yz-plane,
yz-plane, 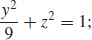 xz-plane,
xz-plane, 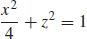
(c)