Chapter 15Printed Page AN-71
1. Vector field
2. False
3. Vectors
4. True
5. The vector field is pictured below. See the Student Solutions Manual for a description.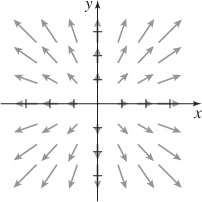
7. The vector field is pictured below. See the Student Solutions Manual for a description.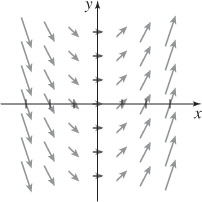
9. The vector field is pictured below. See the Student Solutions Manual for a description.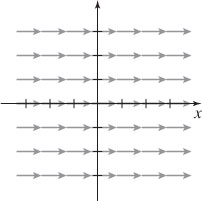
11. The vector field is pictured below. See the Student Solutions Manual for a description.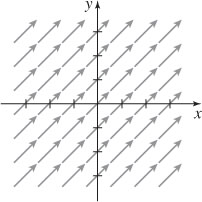
13. The vector field is pictured below. See the Student Solutions Manual for a description.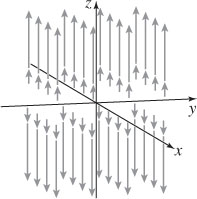
15. The vector field is pictured below. See the Student Solutions Manual for a description.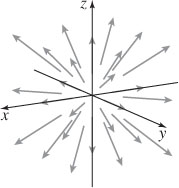
17. ∇f(x,y)=sinyi+(xcosy−siny)j
19. ∇f(x,y,z)=(2xy+y)i+(x2+x+2yz)j+y2k
21. See Student Solutions Manual.
1. True
2. 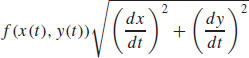
3. False
4. 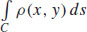
5. False
6. True
7. 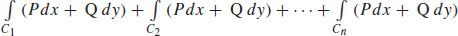
8. False
9. 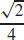
11. 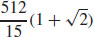
13. 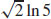
15. 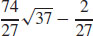
17. π
19. (a) 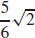
(b) 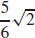
21. (a) 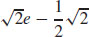
(b) 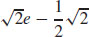
23. 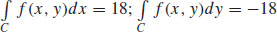
25. 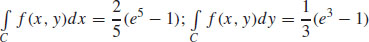
27. (a) 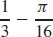
(b) 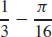
29. (a) 5
(b) 6.15
31. 3
33. 0
35. 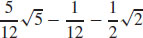
37. 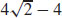
39. 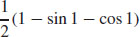
41. 1
43. −128
45. −128
47. 3
49. 
51. 0
53. 
55. π
57. 1
59. 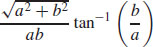
61. 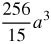
63. 2πa + a2π
65. 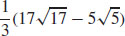
67. 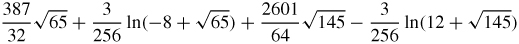
69. 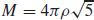
71. 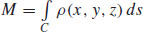
73. M = 20π + 40π2
75. See Student Solutions Manual.
77. 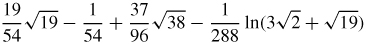
79. See Student Solutions Manual.
81. (a and b) See Student Solutions Manual.
1. False
2. (d)
3. True
4. (c)
5. Closed
6. 0
7. False
8. True
9. False
10. True
11. False
12. 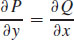
13. (a) 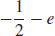
(b) 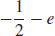
(c) 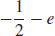
15. 8
17. 108
19. ln 13 − ln 5
21. 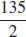
23. 
25. 8
27. 0
29. 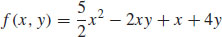 + K
+ K
31. f(x, y) = x ln y + x2 + K
33. f is a conservative vector field.
35. f is a conservative vector field.
37. (a) 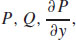 and
and 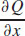 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 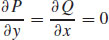 .
.
(b) 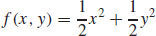 + K
+ K
(c) 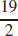
39. (a) 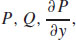 and
and 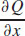 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 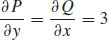 .
.
(b) 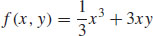 + K
+ K
(c) 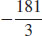
41. (a) 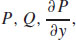 and
and 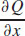 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 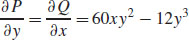 .
.
(b) f (x, y) = x4 + 10x2y3 − 3xy4 + y5 + K
(c) 9
43. (a) 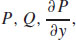 and
and 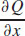 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 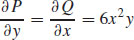 .
.
(b) f(x, y) = x3y2 + K
45. (a) 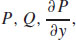 and
and 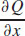 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 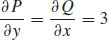 .
.
(b) 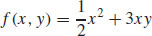 + K
+ K
47. (a) 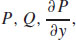 and
and 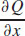 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 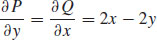 .
.
(b) f(x, y) = x2y − xy2 + K
49. (a) 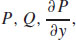 and
and 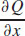 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 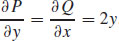 .
.
(b) 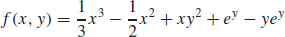 + K
+ K
51. (a) 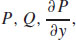 and
and 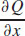 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 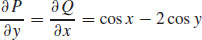 .
.
(b) f(x, y) = y sin x − 2x sin y + K
53. (a) 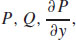 and
and 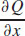 are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and
are continuous everywhere in the xy-plane, and 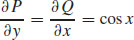 .
.
(b) f(x, y) = x2 + y sin x + K
55. 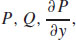 and
and 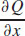 are continuous everywhere in the rectangle, and
are continuous everywhere in the rectangle, and 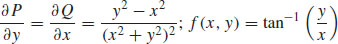 + K
+ K
57. (a) See Student Solutions Manual.
(b) 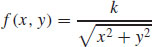 + K
+ K
59. See Student Solutions Manual.
1. Energy
2. True
3. False
4. (d)
5. motion; position
6. False
7. 1
9. 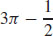
11. 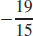
13. 
15. 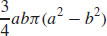
17. 0
19. 
21. 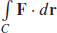 along the first path is 0.
along the first path is 0. 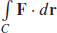 along the second path is −1.
along the second path is −1.
23. 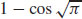
25. The work done is 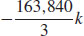 , where k is a constant of proportionality.
, where k is a constant of proportionality.
27. 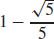
29. 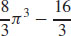
31. See Student Solutions Manual.
33. (a) See Student Solutions Manual.
(b) The escape speed for Earth is 11.2 kilometers per second.
(c) The escape speed for Mars is 5.0 kilometers per second.
(d) The escape speed for the sun is 617.6 kilometers per second.
1. line; double
2. 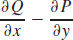
3. False
4. Area
5. −12
7. −12
9. 0
11. 
13. 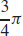
15. 0
17. 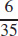
19. 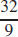
21. −2π
23. −2π
25. 
27. 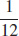
29. 2
31. 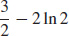
33. 3π
35. See Student Solutions Manual.
37. 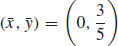
39. 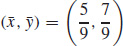
41. 0
43. 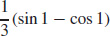
45. Answers will vary.
47. Answers will vary.
49. See Student Solutions Manual.
51. Any piecewise smooth, simple closed curve not passing through the origin and not containing the origin in its interior.
53. See Student Solutions Manual.
55. See Student Solutions Manual.
1. (b)
2. (c)
3. (c)
4. (a)
5. (a) For u = 0: the line r(0,v) = −5v i+(1+v)k; for υ = 0: the line r (u,0) = ui+2u j+(1−u)k.
(b) x+2y+5z = 5
7. (a) For u = 0: the point (0, 0, 0); for υ = 0: the line r(u,0) = u i + uk.
(b) x2 + y2 = z2, 0 ≤ z ≤ 2
9. 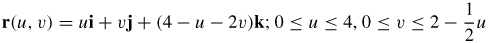
11. r (u, υ) ui + υ j +sin (u2 υ)k; −1 ≤ u ≤ 2, u2 ≤ υ ≤ u + 2
13. (a) 10x − 2y − 5z = 40
(b) r(t) = (7 + 10t) i + (5 − 2 t) j + (4 − 5t) k
15. (a) 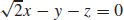
(b) 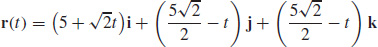
17. 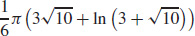
19. 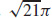
21. 16 π
23. (E)
25. (B)
27. (D)
29. r(u, υ) = 4 cos u i + 4 sin u j + υk; 0 ≤ u ≤ 2π, 0 ≤ υ ≤ 3
31. (a) 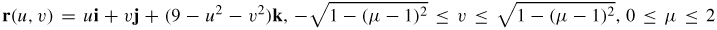
(b)
r(r,θ)=rcosθi+rsinθj+(9−r2)k; 0≤r≤2,−π2≤θ≤π2
33. (a) 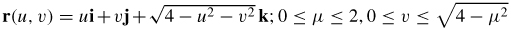
(b) 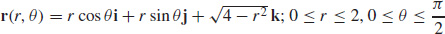
(c) 
35. (a) z = 1
(b) 
37. 
39. (a) r(θ, φ) = cos(θ) sin(φ)i + 3 sin(θ) sin(φ)j + 2 cos(φ)k; 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π, 0 ≤ φ ≤ π
(b) See Student Solutions Manual.
(c)
S=∫2π0∫π0√36cos2θsin4ϕ+4sin2θsin4ϕ+9sin2ϕcosϕdϕdθ
41. (a) 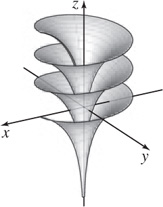
(b) 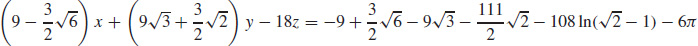
(c) 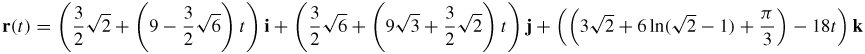
43. (a) r(u, υ) = (b + a cos u) cos υi + (b + a cos u) sin υj + a sin uk
(b) 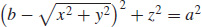
45. See Student Solutions Manual.
47.
(a) r(u, υ) = a cosh ui + (b sinh u cos υ)j + (c sinh u sin υ)k
(b) 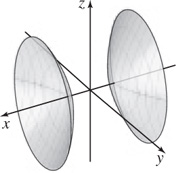
1. (c)
2. (b)
3. 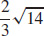
5. 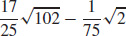
7. 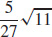
9. 0
11. 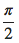
13. 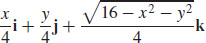
15. 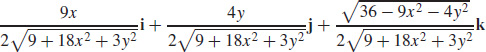
17. 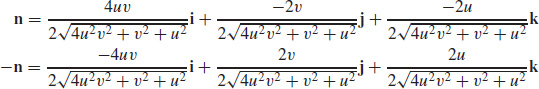
19. ρ
21. 0
23. 3ρ
25. 3ρ
27. 2π
29. 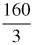
31. −5
33. 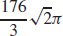
35. 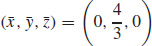
37. 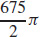
39. 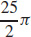
41. See Student Solutions Manual.
43. 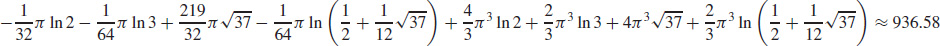
45. 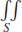 F · ndS is equal to the surface area of S.
F · ndS is equal to the surface area of S.
1. False
2. 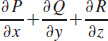
3. div F = 2x+2y+2z
5. div F = 4
7. div 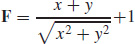
9. 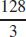
11. 3
13. 80π
15. 4π
17. 
19. See Student Solutions Manual.
21. 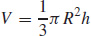
23. 4000π
25. See Student Solutions Manual.
27. See Student Solutions Manual.
29. 2π
31. See Student Solutions Manual.
33. See Student Solutions Manual.
1. False
2. −xi − yj + (2z + 2)k
3. (c)
4. False
5. 2ω
6. False
7. curl F = 0
9. curl F = −xi + xyj + (z − xz)k
11. curl F = −y2cos zi + (6xyz − e2z)j − 3xz2k
13. curl 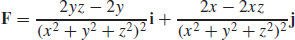
15. curl F = −zexz j
17. curl F = −i − j − k
19. 2π
21. −2π
23. π
25. 0
27. 0
29. 4π
31. curl F = 0. Force F is a conservative vector field.
33. curl F ≠ 0. Force F is not a conservative vector field.
35. 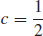
37. See Student Solutions Manual.
39. 0
41. curl F = −2 k. Answers for paths may vary.
43. See Student Solutions Manual.
45. Force F is a conservative vector field. The work done is 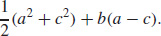
47. See Student Solutions Manual.
49. See Student Solutions Manual.
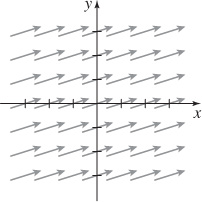
29. 
3. 
5. (a) 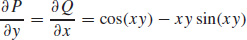
(b) sin 1
7. −2
9. (a) ∇ f (x, y) = F(x, y)
(b) 62
11. 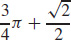
13. 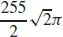
15. 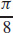
17. π
19. 108
21. −2
23. 12π
25. 7π
27. r(θ, z) = (5 cos θ)i + (2 sin θ)j + zk; 0 ≤ θ ≤ 2π, 1 ≤ z ≤ 6
29. 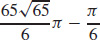
31. 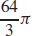
33. 0
35. 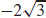
37. (a) div F = −z sin x + cos y
(b) curl F = (cos x − ex)j
(c) 0
39. (a) div F = 3
(b) curl F = 0
(c) 0
41. 0
43. 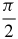
45. 
47. F is not a conservative vector field because curl F ≠ 0.