7.2 Integrals Containing Trigonometric FunctionsPrinted Page 480
OBJECTIVES
When you finish this section, you should be able to:
In this section, we develop techniques to find certain trigonometric integrals. When studying these techniques, concentrate on the strategies used in the examples rather than trying to memorize the results.
1 Find Integrals of the form ∫sinnxdx or ∫cosnxdx, n≥2 an IntegerPrinted Page 480
Although we could use integration by parts to obtain reduction formulas for integrals of the form ∫sinnxdx or ∫cosnxdx, n≥2 an integer, these integrals also can be found using other, often easier, techniques. We consider two cases:
- n≥3 an odd integer
- n≥2 an even integer.
Suppose we want to find ∫sinnx dx when n≥3 is an odd integer. We begin by writing the integral in the form ∫sinnx dx=∫sinn−1xsinx dx
Since n is odd, (n−1) is even and we can use the identity sin2x=1−cos2x.
Then the substitution u=cosx, du=−sinx dx, leads to an integral involving integer powers of u.
481
EXAMPLE 1Finding the Integral ∫sin5xdx
Find ∫sin5xdx.
NEED TO REVIEW?
The method of substitution is discussed in Section 5.6, pp. 387-393.
Solution Since the exponent 5 is odd, we write ∫sin5xdx=∫sin4xsinxdx, and use the identity sin2x=1−cos2x. ∫sin5xdx=∫sin4xsinxdx=∫(sin2x)2sinxdx=∫(1−cos2x)2sinxdx=∫(1−2cos2x+cos4x)sinxdx
Now we use the substitution u=cosx. Then du=−sinxdx, and ∫sin5xdx=−∫(1−2u2+u4) du=−u+23u3−15u5+C=−cosx+23cos3x−15cos5x+C
A similar technique is used to find ∫cosnxdx, when n≥3 is an odd integer. In this case, we write ∫cosnxdx=∫cosn−1xcosxdx
and use the trigonometric identity cos2x=1−sin2x. Then we use the substitution u=sinx. For example, ∫cos3x dx=∫cos2xcosxdx=∫(1−sin2x)cosxdx=↑u=sinxdu=cosxdx∫(1−u2) du=u−u33+C=sinx−sin3x3+C
NOW WORK
To find ∫sinnxdx or ∫cosnxdx when n≥2 is an even integer, the preceding strategy does not work. (Try it for yourself.) Instead, we use one of the identities below: sin2x=1−cos(2x)2cos2x=1+cos(2x)2
to obtain a simpler integrand.
NEED TO REVIEW?
Trigonometric identities are discussed in Appendix A.4, pp. A-32 to A-35.
EXAMPLE 2Finding the Integral ∫sin2xdx
Find ∫sin2xdx.
Solution Since the exponent of sinx is an even integer, we use the identity sin2x=1−cos(2x)2
Then ∫sin2xdx=12∫[1−cos(2x)]dx=12∫dx−12∫cos(2x)dx=12x+C1−12∫cosudu2u=2x,du=2dx.=12x+C1−14sin(2x)+C2
482
Since C1 and C2 are constants, we write the solution as ∫sin2xdx=12x−14sin(2x)+C
where C=C1+C2.
NOTE
Usually we will just add the constant of integration at the end of the integration to avoid letting C=C1+C2.
NOW WORK
EXAMPLE 3Finding the Average Value of a Function
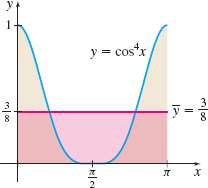
Find the average value ˉy of the function f(x)=cos4x over the closed interval [0,π].
NEED TO REVIEW?
The average value of a function is discussed in Section 5.4, pp. 373-374.
Solution The average value ˉy of a function f over [a,b] is ˉy=1b−a∫baf(x)dx.
For f(x)=cos4x on [0,π], we have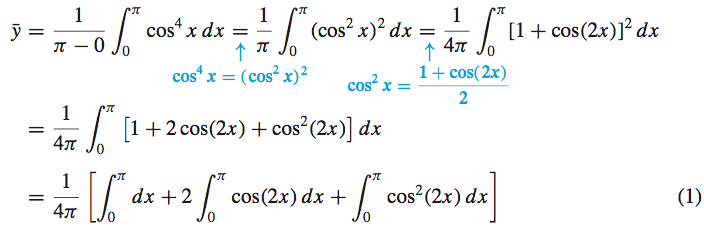
Now 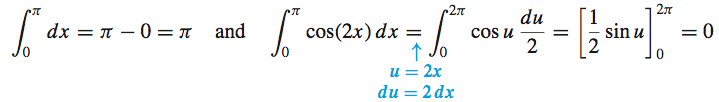
To find ∫π0cos2(2x)dx, we use the identity cos2θ=1+cos(2θ)2 again to write cos2(2x)=1+cos(4x)2. Then ∫π0cos2(2x)dx=∫π01+cos(4x)2dx=12[∫π0dx+∫π0cos(4x)dx]=12[π+∫4π0cosudu4]u=4x; du=4dx
So, from (1), ˉy=14π[π+0+π2]=38
If f is nonnegative on an interval [a,b], the average value of f over the interval [a,b] represents the height of a rectangle with width b−a whose area equals the area under the graph of f from a to b. Figure 2 shows the graph of f from Example 3 and the rectangle of height ˉy=38 and base π whose area is equal to the area under the graph of f.
NOW WORK
2 Find Integrals of the Form ∫sinmxcosnxdxPrinted Page 483
483
Integrals of the form ∫sinmxcosnxdx are found using variations of previous techniques. We discuss two cases:
- At least one of the exponents m or n is a positive odd integer.
- Both exponents are positive even integers.
EXAMPLE 4Finding the Integral ∫sin5x√cosxdx
Find ∫sin5x√cosxdx=∫sin5xcos1/2xdx.
Solution The exponent of sinx is 5, a positive, odd integer. We factor sinx from sin5x and write ∫sin5xcos1/2xdx=∫sin4xcos1/2xsinxdx=∫(sin2x)2cos1/2xsinxdx=∫(1−cos2x)2cos1/2xsinxdx
Now we use the substitution u=cosx. ∫sin5xcos1/2xdx=∫(1−cos2x)2cos1/2xsinxdx=↑u=cosxdu=−sinx dx∫(1−u2)2u1/2(−du)=−∫(u1/2−2u5/2+u9/2)du=−23u3/2+47u7/2−211u11/2+C=u3/2[−23+47u2−211u4]+C=↑u=cosx(cosx)3/2[−23+47cos2x−211cos4x]+C
NOW WORK
If m and n are both positive even integers in ∫sinmxcosnxdx, we use the trigonometric identity sin2x+cos2x=1 to obtain a sum of integrals, each integral involving only even powers of either sinx or cosx. For example, ∫sin2xcos4xdx=∫(1−cos2x)cos4xdx=∫cos4xdx−∫cos6xdx
The two integrals on the right are now of the form ∫cosnxdx, n a positive even integer, and we can integrate them using the techniques discussed in Examples 2 and 3.
3 Find Integrals of the Form ∫tanmx secnx dx or ∫cotmxcscnx dxPrinted Page 483
We consider three cases involving integrals of the form ∫tanmxsecnxdx:
- The exponent m on the tangent function is a positive odd integer.
- The exponent n on the secant function is a positive even integer.
- The tangent function is raised to a positive even integer m and the secant function is raised to a positive odd integer n.
484
The idea is to express the integrand so that we can use either the substitution u=tanx and du=sec2xdx or the substitution u=secx and du=secxtanxdx, while leaving an even power of one of the functions. Then we use a Pythagorean identity to express the integrand in terms of only one trigonometric function.
EXAMPLE 5Finding the Integral ∫tan3xsec4xdx
Find ∫tan3xsec4xdx.
Solution Here, tanx is raised to the odd power 3. We factor tanx from tan3x and use the identity tan2x=sec2x−1. ∫tan3xsec4xdx=∫tan2xtanxsec4xdxFactor tan x from tan3x.=∫(sec2x−1)tanxsec4xdxtan2x=sec2x−1=∫(sec2x−1)sec3xsecxtanxdxFactor sec x from sec4x.=∫(u2−1)u3duSubstitute u=secx;du=secx tanxdx.=∫(u5−u3)du=u66−u44+C=↑u=secxsec6x6−sec4x4+C
NOW WORK
EXAMPLE 6Finding the Integral ∫tan2xsec4xdx
Find ∫tan2xsec4xdx.
Solution Here, secx is raised to a positive even power. We factor sec2x from sec4x and use the identity sec2x=1+tan2x. Then ∫tan2xsec4xdx=∫tan2xsec2x⋅sec2xdxFactor sec2x from sec4x.=∫tan2x(1+tan2x)sec2xdxsec2x=1+tan2x=∫u2(1+u2)duSubstitute u=tanx;du=sec2xdx.=∫(u2+u4)du=u33+u55+C=↑u=tanxtan3x3+tan5x5+C
NOW WORK
When the tangent function is raised to a positive even integer m and the secant function is raised to a positive odd integer n, the approach is slightly different. Rather than factoring, we begin by using the identity tan2x=sec2x−1.
485
EXAMPLE 7Finding the Integral ∫tan2xsecxdx.
Find ∫tan2xsecxdx.
Solution Here, tan x is raised to an even power and sec x to an odd power. We use the identity tan2x=sec2x−1 to write ∫tan2xsecxdx=∫(sec2x−1)secxdx=∫(sec3x−secx) dx=∫sec3xdx−∫secxdx
Next we integrate ∫sec3xdx by parts. Choose u=secxanddv=sec2xdxdu=secxtanxdxv=∫sec2xdx=tanx
Then ∫sec3xdx=secxtanx−∫tan2xsecxdx∫udv=uv−∫vdu=secxtanx−∫(sec2x−1)secxdxtan2x=sec2x−1=secxtanx−∫sec3xdx+∫secxdxWrite the integral as thesum of two integrals.2∫sec3xdx=secxtanx+∫secxdxAdd ∫sec3x dx to both sides.∫sec3xdx=12[secxtanx+ln|secx+tanx|]Solve for ∫sec3x dx;∫secx dx=ln|secx+tanx|.
Now we substitute this result in (2). ∫tan2xsecxdx=∫sec3xdx−∫secxdx=12[secxtanx+ln|secx+tanx|]−ln|secx+tanx|+C=12[secxtanx−ln|secx+tanx|]+C
NOTE
Substituting n=3 into the reduction formula for ∫secnxdx (derived in Example 8 of Section 7.1) could also have been used to find ∫sec3xdx.
NOW WORK
To find integrals of the form ∫cotmxcscnxdx, we use the same strategies, but with the identity csc2x=1+cot2x.
4 Find Integrals of the Form ∫sin(ax) sin(bx)dx, ∫sin(ax)cos(bx)dx, or ∫cos(ax)cos(bx)dxPrinted Page 485
Trigonometric integrals of the form ∫sin(ax)sin(bx)dx∫sin(ax)cos(bx)dx∫cos(ax)cos(bx)dx
are integrated using the product-to-sum identities:
- 2sinAsinB=cos(A−B)−cos(A+B)
- 2sinAcosB=sin(A+B)+sin(A−B)
- 2cosAcosB=cos(A−B)+cos(A+B)
These identities transform the integrand into a sum of sines and/or cosines.
486
EXAMPLE 8Finding the Integral ∫sin(3x)sin(2x)dx
Find ∫sin(3x)sin(2x)dx.
Solution We use the product-to-sum identity 2sinAsinB=cos(A−B)−cos(A+B).
Then 2sin(3x)sin(2x)=cos(3x−2x)−cos(3x+2x)sin(3x)sin(2x)=12[cosx−cos(5x)]
Then ∫sin(3x)sin(2x)dx=12∫[cosx−cos(5x)]dx=12∫cosx dx−12∫cos(5x)dx=↑u=5xdu=5 dx12sinx−12∫cosudu5=12sinx−110sin(5x)+C